
What Is Access Control: Your Complete Security Roadmap
Share
Understanding What Is Access Control: The Security Game-Changer

Access control lies at the heart of security. It determines who can access specific resources, when they can access them, and what they're permitted to do with those resources. Think of it as a highly adaptable security guard for your digital and physical assets, controlling the flow of access and permissions.
Access control isn't about simple locks and keys anymore. It's evolved into a sophisticated system of digital gatekeeping. Imagine a company's confidential customer data. Access control ensures only authorized personnel, such as customer service representatives, can view and interact with this sensitive information, preventing unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Different Levels of Access: A Tiered Approach
Access control frequently uses a tiered approach. This system grants varying levels of access based on individual roles and responsibilities within an organization. A CEO might have access to all company data, while a marketing intern's access might be limited to marketing-related files.
This granular control is essential for protecting sensitive information and maintaining efficient operations. Here's a breakdown of the typical tiers:
- Basic Access: This level grants limited access to specific resources.
- Elevated Access: This offers increased permissions based on departmental needs.
- Administrative Access: This level provides full control over designated systems or data.
Why Is Access Control Essential? The Security Imperative
Effective access control significantly reduces security risks and incidents. It acts as the first line of defense against unauthorized access to sensitive information or critical systems. It's a fundamental part of a robust security strategy.
Furthermore, access control plays a vital role in regulatory compliance. Many industries have strict regulations concerning data privacy and security. Implementing strong access control helps organizations meet these essential requirements.
In our increasingly interconnected world, with a growing reliance on cloud computing and remote work, strong access control is more important than ever. The global access control market has experienced significant growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing security needs.
As of 2024, the market size was estimated at USD 10.76 billion. Projections for 2025 indicate a rise to approximately USD 11.56 billion, demonstrating a strong and growing demand for access control solutions.
This growth is fueled by the integration of AI and machine learning into access control systems. These technologies enhance security capabilities through real-time threat detection and predictive analytics. Find more detailed statistics here.
Practical Applications: Real-World Examples
Access control isn't just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications across diverse sectors. In healthcare, it ensures patient data confidentiality. In finance, it protects sensitive financial transactions. In government, it safeguards classified information.
These are just a few examples of how access control provides tangible benefits in various real-world scenarios. Its applications are vast and constantly expanding.
By understanding and implementing robust access control measures, organizations can significantly improve their security posture and protect themselves from ever-evolving threats. This leads to a more secure and efficient operating environment, safeguarding valuable assets and maintaining a competitive edge in today's business landscape.
Choosing The Right Access Control System For Your Needs
Not all access control systems are created equal. Selecting the wrong one can have a significant impact on your security and your budget. This section explains the core differences between physical access control systems (PACS), logical access control systems (LACS), and hybrid solutions. Understanding these distinctions is the first step towards a well-informed decision.
Types of Access Control: A Quick Overview
The infographic below visualizes the three main categories of access control and how they manage permissions.
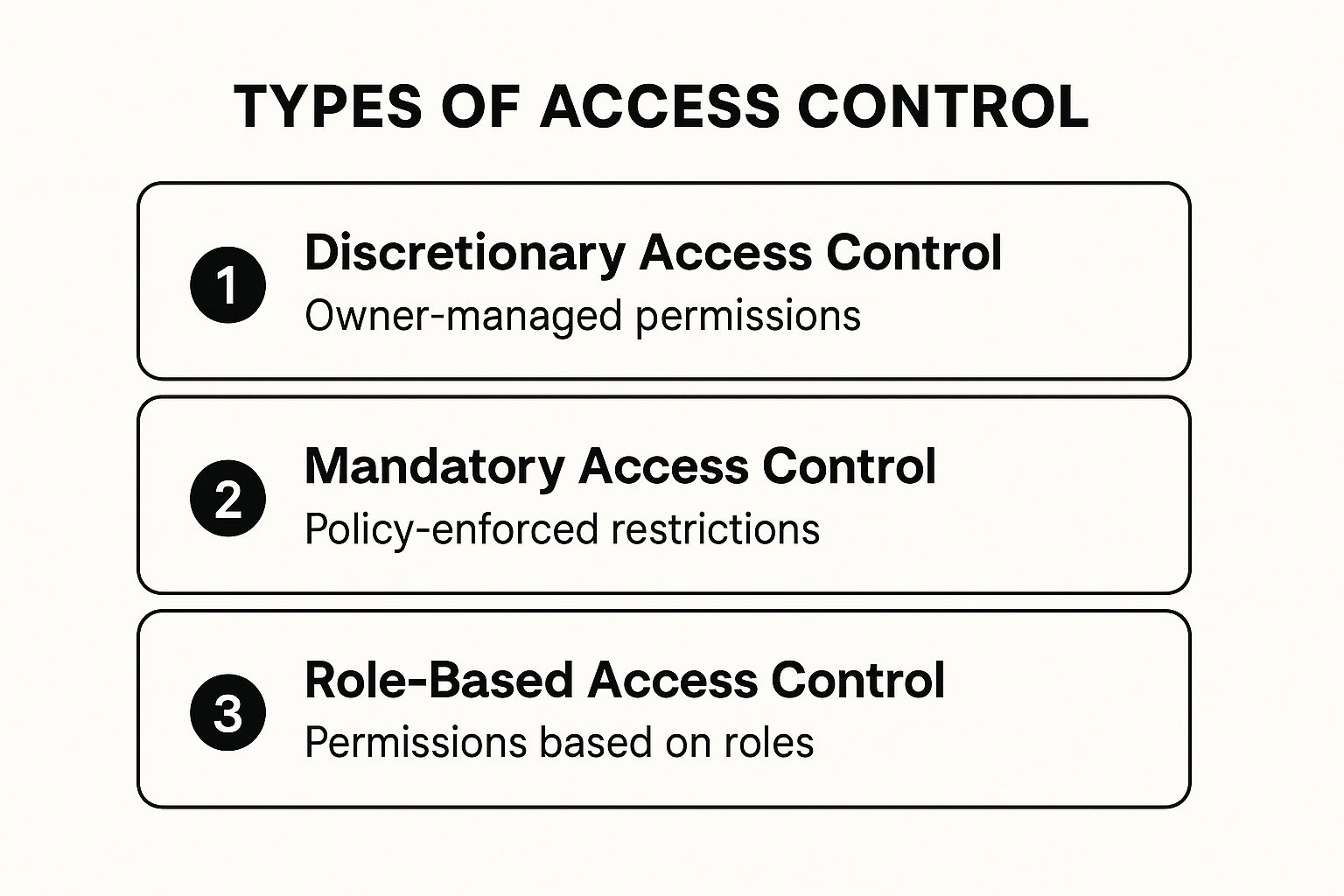
As the infographic illustrates, each access control type offers a unique approach to permission management. These range from the individualized control of Discretionary Access Control to the more rigid, policy-based Mandatory Access Control, and the structured Role-Based Access Control. This understanding lays the groundwork for exploring the specifics of each system and its practical uses.
Physical Access Control Systems (PACS)
Physical access control systems manage physical access to buildings and secured areas. This encompasses everything from simple key card readers to advanced biometric scanners in high-security zones. These systems are designed to prevent unauthorized entry, protecting personnel and assets. For example, a data center might employ a PACS with multi-factor authentication, combining biometric scans and key cards to restrict entry to authorized personnel only.
Logical Access Control Systems (LACS)
Logical access control systems protect digital resources. They manage who can access networks, data, and systems by regulating user accounts, passwords, and permissions. LACS are crucial for safeguarding sensitive information. For instance, a company might implement a LACS that requires employees to use strong passwords combined with multi-factor authentication when accessing the company network.
Hybrid Access Control Systems
Hybrid access control systems combine the features of both physical and logical access control. This integrated approach offers a more comprehensive security strategy. A university, for example, might use a hybrid system to manage physical access to campus buildings alongside digital access to student information systems. This unified system could mean a single student ID card grants both physical access to buildings and digital access to the university's online learning platform.
Choosing the Best Fit
The most effective access control system depends on individual needs and security requirements. A small business might find a basic physical access control system sufficient. A large corporation with multiple locations and sensitive data, on the other hand, may require a more complex hybrid system.
To help guide your decision, we've compiled a comparison table summarizing key features and considerations for each access control system type:
Access Control System Comparison Guide A comprehensive breakdown of different access control systems with real-world performance data and implementation considerations
| System Type | Security Level | Cost Range | Best Use Cases | Maintenance Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Access Control Systems (PACS) | Low to High (Depending on implementation) | Varies widely based on complexity | Securing physical locations, restricting access to sensitive areas, managing building entry/exit | Regular inspections, hardware maintenance, software updates |
| Logical Access Control Systems (LACS) | Low to High (Depending on implementation) | Varies based on software and features | Protecting digital resources, managing user access to networks and data | Regular software updates, security audits, password management |
| Hybrid Access Control Systems | High (Combines physical and logical security) | Typically higher due to integration complexity | Organizations requiring both physical and logical security, managing access across multiple systems | Ongoing maintenance of both physical and logical components, integration support |
This table provides a quick overview of the different access control systems and their key features. By comparing these features, organizations can better understand which system best suits their specific security needs.
Factors to consider when choosing an access control system include:
- The level of security required: Higher security needs necessitate more advanced systems.
- The budget: Cost is an important consideration for any organization.
- Ease of use: The system should be user-friendly for both administrators and end-users.
- Integration with existing systems: Compatibility with current infrastructure is key for streamlined operation.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose an access control system that effectively addresses your security needs and budget constraints. This strategic approach will contribute to building a robust and effective security infrastructure to protect your valuable assets and information.
The Essential Components That Make Access Control Work

Behind every effective access control system is a network of interconnected parts working together to provide robust security. This article explores the core elements of access control, from the obvious to the less visible, explaining how they contribute to a comprehensive security solution.
Authentication Methods: Proving Your Identity
Authentication, the process of verifying a user's identity, is at the heart of access control. Several methods achieve this, each with its pros and cons.
-
Credentials: These are physical items like key cards, fobs, or traditional keys. They offer a tangible form of identification.
-
Biometrics: This method uses unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans. Biometrics offer enhanced security.
-
Passwords and PINs: While still common, these are vulnerable if not managed carefully.
The best authentication method depends on the security level needed and the budget. Higher security often means using more complex methods.
Credential Readers: Granting Entry
Credential readers are the gatekeepers, interacting with credentials to grant or deny access. They range from basic card readers to advanced biometric scanners.
Different readers work with different credential types. A magnetic stripe reader suits traditional key cards, while biometric authentication needs a fingerprint scanner. The reader must match the authentication method.
Control Panels: The Central Nervous System
Control panels form the central hub, receiving information from credential readers and signaling locks, alarms, or other devices. The control panel is the system's brain, making decisions based on programmed rules and access rights.
Modern control panels often boast advanced features such as real-time monitoring, event logging, and integration with other security systems like those provided by Genetec. This centralized approach enhances security and provides valuable insights into access activity.
Management Software: Overseeing the Entire Operation
Access control management software offers a user-friendly interface for managing the whole system. Administrators use this software to create accounts, assign permissions, generate reports, and monitor system activity. Effective software is crucial for maintaining a secure and organized system.
Modern software often includes remote access management, automated reporting, and integration with other business systems. This streamlines management and reduces administrative work. Check out our guide on How to master user permissions management and boost security and efficiency.
The Importance of Redundancy and Backup Systems
An access control system's reliability depends on redundancy and backups. These ensure continued operation during power failures or system issues. Backup power supplies and redundant communications prevent single points of failure, ensuring the system works when needed most.
This reliability is especially vital for critical infrastructure or high-security locations where uninterrupted access control is essential. This focus on reliability underscores the importance of a well-designed access control system for maintaining a secure environment.
Measurable Benefits That Transform Your Security Approach

Access control is more than just locking doors. It offers tangible benefits that significantly improve your overall security and operational efficiency. This translates to better security, lower costs, and deeper insights into how your facilities are used.
Reduced Security Incidents: A Proactive Approach
One of the most significant benefits of access control is its proactive risk mitigation. By controlling who accesses what, when, and where, organizations can dramatically reduce the likelihood of security breaches. This proactive approach stops incidents before they happen, rather than reacting after the fact.
These benefits translate into real-world results. Organizations using comprehensive access control systems report an average 67% reduction in security incidents, with 84% achieving full ROI within 18 months. These improvements come from reduced theft, improved operational efficiency, and the elimination of traditional key management expenses. Find more detailed statistics here.
Eliminating Key Management Headaches: Streamlined Efficiency
Traditional key management is often a logistical challenge, involving considerable administrative overhead and security vulnerabilities. Access control systems eliminate these issues by replacing physical keys with digital credentials. This simplifies administration, reduces costs related to lost keys, and boosts overall security. This increased efficiency saves time and money while minimizing unauthorized access.
Gaining Visibility into Facility Usage Patterns: Data-Driven Insights
Access control systems provide valuable data on facility usage. This information can be used to optimize space, improve efficiency, and enhance security protocols. Analyzing access logs helps organizations identify peak usage times, underutilized areas, and potential security weaknesses. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
Real-Time Monitoring and Proactive Responses: Enhanced Security
Real-time monitoring allows security personnel to respond proactively to potential threats. The system provides immediate alerts for unauthorized access attempts, suspicious behavior, or system malfunctions. This real-time awareness empowers security teams to intervene quickly, minimizing potential damage and maintaining a secure environment.
Simplified Compliance Reporting and Incident Investigations: Streamlined Processes
Access control systems create detailed audit trails of all access activity. This simplifies compliance reporting by readily documenting who accessed what and when. These audit trails are also crucial during incident investigations, providing essential evidence for identifying those responsible and understanding what happened.
Operational Efficiencies: Surprising Benefits
Beyond improved security, access control systems provide a range of operational efficiencies. These include streamlined visitor management, flexible access scheduling, and automated integration with HR systems. These improvements free up staff time, reduce administrative burdens, and improve overall organizational efficiency.
ROI and Realistic Timelines: Honest Discussions
While access control benefits are clear, understanding ROI and implementation timelines is important. Many organizations see a return on investment quickly due to fewer security incidents, lower administrative costs, and improved operational efficiencies. However, realistic timelines depend on the system’s complexity, organization size, and specific features.
Streamlined Visitor Management: Enhanced Professionalism
Access control systems can significantly improve visitor management, creating a more professional and secure environment. Features like automated visitor registration, badge printing, and real-time tracking increase security and offer a more welcoming guest experience.
Flexible Access Scheduling: Adapting to Change
Modern access control systems offer flexible scheduling. This lets organizations easily grant or revoke access based on individual needs, time of day, or specific events. This flexibility is essential for businesses with evolving staffing needs, shift patterns, or temporary access requirements.
By understanding these diverse benefits, organizations can make informed decisions about implementing a system that best suits their security and operational needs. This approach not only protects valuable assets but also contributes to a more efficient and secure operating environment.
Implementation Strategies That Actually Work
Implementing an access control system isn't just about buying the right equipment. It takes careful planning and flawless execution. This section shares proven strategies from organizations that nailed their access control implementation on the first try. We'll explore everything from initial assessments to encouraging user adoption, and how to sidestep those common pitfalls along the way.
Planning Your Access Control Implementation
The first step is a thorough security assessment. This process pinpoints vulnerabilities and defines your organization's specific security needs. Be sure to consider both physical and digital assets, as well as potential threats. This assessment informs the type of access control system you'll need—physical, logical, or a hybrid solution.
Budget planning is also crucial. Accurately forecasting costs—hardware, software, installation, and ongoing maintenance—is essential. Unforeseen expenses can quickly derail a project, so a well-defined budget is your project's bedrock. Don't forget those long-term costs like system upgrades and future expansions.
You might be interested in: How to master effective group access control, secure, and streamline.
Vendor Selection and System Design
Vendor evaluation is another critical piece of the puzzle. Research various vendors like Genetec, compare their products and services, and select one with a proven track record and solid support. Scalable solutions are key—choose a system that can adapt to your future needs and grow alongside your organization.
After choosing a vendor, the next step is designing the system architecture. This involves selecting the right credentials, readers, and control panels. It also includes mapping access points, defining security levels for different areas, and ensuring seamless integration with your existing infrastructure.
Implementation and User Adoption
A phased rollout is often the best implementation strategy. Begin with a pilot program in a contained area to thoroughly test the system and iron out any wrinkles. Then, gradually expand the system to other areas, minimizing disruptions to daily operations. This allows for adjustments before a full-scale deployment.
Change management is essential for user adoption. Train your staff on the new system, address their questions, and alleviate any concerns. Clear communication and comprehensive training ensure a smooth transition and maximize the system’s benefits. This includes establishing clear procedures for access requests, issue reporting, and credential management.
Measuring Success and Ongoing Maintenance
Post-implementation, establish metrics to gauge the system’s effectiveness. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as security incidents, system uptime, and user satisfaction. Regular system maintenance is also paramount. Schedule routine inspections, software updates, and hardware maintenance to ensure peak performance and prevent potential issues. This proactive approach helps identify areas for improvement and ensures the system continues meeting your security needs.
To help visualize the implementation process, we’ve prepared a roadmap outlining key phases, activities, and success factors:
A step-by-step guide to successful access control deployment with key milestones and proven best practices is provided below.
| Phase | Duration | Key Activities | Critical Success Factors | Common Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 2-4 Weeks | Security Assessment, Budget Planning | Clear Objectives, Stakeholder Buy-in | Scope Creep, Budgetary Constraints |
| Vendor Selection | 4-6 Weeks | Vendor Evaluation, System Design | Due Diligence, Contract Negotiation | Integration Issues, Vendor Lock-in |
| Implementation | 4-8 Weeks | Phased Rollout, Change Management | User Training, Communication Plan | Technical Glitches, User Resistance |
| Ongoing Maintenance | Ongoing | Performance Monitoring, System Maintenance | Proactive Approach, Dedicated Resources | Budget Constraints, Lack of Expertise |
This table provides a high-level overview. The specific duration and activities will vary based on the complexity of your project and the specific needs of your organization.
By following these strategies, you can ensure a smooth and successful access control implementation, maximizing security and minimizing disruption. This proactive approach lays the foundation for a robust and effective access control system, contributing to a more secure and efficient environment.
Future-Proofing Your Access Control Investment
The world of access control is constantly evolving. Staying ahead requires a keen understanding of emerging trends and a strategic approach to investment. This means looking beyond current solutions and anticipating the technologies that will shape the future of security. This section explores these trends, helping you prepare for what's next and make informed decisions that will protect your organization for years to come.
Emerging Trends in Access Control
Several key trends are transforming the access control landscape:
-
AI-Powered Threat Detection: Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing security by analyzing access patterns and identifying anomalies in real-time. This proactive approach empowers security teams to respond to potential threats before they escalate. For example, AI can detect unusual login attempts outside of normal business hours or from unrecognized devices, triggering immediate alerts and facilitating swift intervention.
-
Cloud-Based Management Platforms: Cloud platforms offer scalable and flexible access control management. They enable centralized control over multiple locations, simplify system administration, and offer seamless integration with other security systems. Centralized management streamlines IT operations while bolstering security.
-
Mobile Credentials: Smartphones are replacing traditional key cards and fobs, offering a more convenient and secure access method. This shift reflects the growing use of personal devices for authentication. Mobile credentials offer enhanced security features, including two-factor authentication and biometric verification, making them far more secure than traditional keys.
-
Biometric Technology: Biometrics, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, are becoming increasingly affordable and widely adopted. This wider availability empowers organizations of all sizes to implement robust authentication measures. Smaller businesses that previously couldn't justify the cost of biometric systems now have access to cost-effective solutions.
-
Integration with Broader Security Ecosystems: Access control systems are increasingly integrated with other security platforms, including video surveillance and intrusion detection systems. This creates a more comprehensive and responsive security approach, enabling automated reactions to security breaches, such as automatically locking down a building during an intrusion.
Strategic Approaches to Future-Proofing
Navigating the evolving security landscape requires strategic thinking. Here are some key considerations for future-proofing your access control investments:
-
Embrace Open Standards: Choosing systems based on open standards ensures compatibility with a wider range of devices and systems, safeguarding your investment from vendor lock-in.
-
Prioritize Scalability: Select a system that can adapt to your organization's growth. Scalability is essential for meeting changing needs and avoiding costly system replacements.
-
Invest in Cloud Solutions: Cloud-based platforms offer flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making them a wise choice for long-term planning.
-
Stay Informed about Emerging Technologies: Staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in access control enables informed decisions about upgrades and future investments.
-
Plan for Integration: Design your access control system with integration in mind. This approach facilitates connections with other security platforms, strengthening your overall security posture.
The access control market is experiencing consistent growth. Market analysis predicts impressive expansion, with some projections estimating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 9%. One forecast anticipates the market reaching approximately USD 17.37 billion by 2033, while another projects it to reach USD 39.24 billion by 2037. This continued growth is fueled by ongoing technological advancements, evolving regulatory requirements, and the increasing demand for robust security infrastructure. Explore this topic further here.
Read also: Top Access Control Best Practices for 2025 to learn more about maximizing your security efforts.
By understanding these emerging trends and implementing strategic approaches, you can ensure your access control investments remain effective and relevant, protecting your organization from evolving threats and positioning it for long-term security.
Your Access Control Action Plan
Ready to strengthen your security but feeling lost on where to begin? This action plan provides a practical roadmap to access control success, customized for your organization's specific needs and current security posture. We'll walk you through key steps, from conducting detailed security assessments to securing leadership buy-in and selecting the right vendors. This plan will help you quickly showcase the value of access control while establishing comprehensive security coverage.
Assessing Your Security Needs: The First Step
Understanding your current security status is crucial. Conduct a thorough security assessment to identify vulnerabilities and pinpoint your specific needs. Consider both physical and digital assets. Ask yourself key questions: Where are the weaknesses? What are your most valuable assets? Which threats are most relevant to your industry and location? The answers will shape your access control strategy.
For instance, a small retail business will likely focus on preventing theft and managing customer access. However, a large financial institution requires much more stringent security measures for both physical and digital assets, including robust authentication and data protection.
Building Your Business Case: Getting Leadership Buy-In
After identifying your security needs, create a compelling business case to present the value of access control to leadership. Quantify the potential costs of security breaches, emphasizing the financial and reputational damage that can result. On the flip side, highlight the return on investment (ROI) access control offers through fewer incidents, improved efficiency, and better compliance.
Don't forget to emphasize the non-financial benefits, such as improved security, increased employee productivity, and more streamlined operations. Presenting both the tangible and intangible benefits creates a well-rounded picture of access control's value.
Choosing the Right Vendors: Partners in Security
Selecting the right access control vendor is critical. Don't simply opt for the cheapest option. Carefully evaluate various providers, considering factors such as system features, scalability, customer support, and integration capabilities with existing systems. Choose vendors with a proven track record and a commitment to innovation.
View your access control vendor as a long-term partner. Make sure they offer the necessary training, support, and future system upgrades to maintain effectiveness and keep your system up-to-date.
Quick Wins and Long-Term Strategies: A Balanced Approach
Identify quick wins to demonstrate immediate value. Implementing a basic key card system, for example, can rapidly enhance physical security and remove the headaches of managing traditional keys. At the same time, develop a long-term strategy for building a comprehensive access control system. This long-term approach enables phased implementation, gradual upgrades, and integration with other security platforms.
Actionable Checklists and Timelines: Your Implementation Guide
Stay organized and on schedule with checklists and timelines. Develop a realistic timeline for each phase of implementation, from the initial planning stages to the final deployment and ongoing maintenance. Create checklists for each step, ensuring every necessary task is thoroughly completed.
Here's a sample checklist for the initial planning phase:
- Conduct a thorough security assessment
- Define specific security objectives
- Determine budget constraints
- Research potential access control vendors
- Develop a preliminary implementation timeline
This structured method will keep you organized and focused, ensuring your project remains on track and within budget.
Decision Frameworks: Making Informed Choices
Employ decision frameworks to guide your decisions. When evaluating different access control systems, for example, build a comparison table listing the features, costs, and benefits of each option. This side-by-side comparison simplifies the process of identifying the best solution for your specific needs.
Ongoing Optimization: Continuous Improvement
Access control isn't a one-time project; it's an ongoing process. Continuously monitor your system's performance, identify areas for improvement, and adapt to changing security needs. This proactive approach ensures your system remains effective and relevant against evolving threats. Regularly review your security policies, update your systems, and offer consistent training to your staff.
Streamline your digital experience and reduce costs with AccountShare, a platform that allows shared access to premium subscriptions. Securely manage accounts with advanced features like customizable permissions and password sharing. Learn more about AccountShare.
