
8 Critical Remote Work Security Best Practices for 2025
Share
Remote work is no longer a temporary trend; it's a permanent fixture of the modern workplace. While offering unprecedented flexibility, this shift has also expanded the digital attack surface, making robust security measures more critical than ever. Traditional, office-centric security perimeters are obsolete. Today, every home office, co-working space, and coffee shop is a potential entry point for cyber threats.
This article moves beyond generic advice to provide actionable, detailed strategies for securing your distributed workforce. We will explore a comprehensive set of remote work security best practices, from foundational frameworks like Zero Trust to advanced technical controls such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and the indispensable human element of security awareness training. The goal is to build a resilient and secure remote work environment that protects your organization's most valuable assets.
Successfully adapting also means securing every communication channel. Organizations must implement robust strategies for video conferencing security to protect sensitive virtual interactions from unauthorized access and data breaches. By addressing these critical areas, from endpoint protection to secure collaboration, you can confidently navigate the complexities of a decentralized workforce. This guide will provide the specific, in-depth steps needed to fortify your operations.
1. Zero Trust Security Architecture
The traditional "castle-and-moat" security model, where everything inside the corporate network is trusted, is dangerously outdated in the era of remote work. A Zero Trust Security Architecture flips this concept on its head, operating on a simple but powerful principle: never trust, always verify. This model treats every access request as a potential threat, regardless of its origin, and requires strict identity verification and authorization for every user and device trying to access resources.
How It Strengthens Remote Work Security
Instead of a single, hardened perimeter, Zero Trust enforces security at a granular level. It assumes that a breach is inevitable and focuses on minimizing the potential damage. A key component of this approach involves creating small, isolated security zones within the network. This practice is detailed further in guides on implementing network segmentation for security, which helps contain threats and prevent them from moving laterally across your systems.
Major companies like Google (with their BeyondCorp model) and Netflix have successfully implemented Zero Trust to secure their massive, distributed workforces. For any organization adopting remote work security best practices, this architecture is a foundational step.
To understand the core pillars of this model, consider this quick reference guide visualizing its key principles.
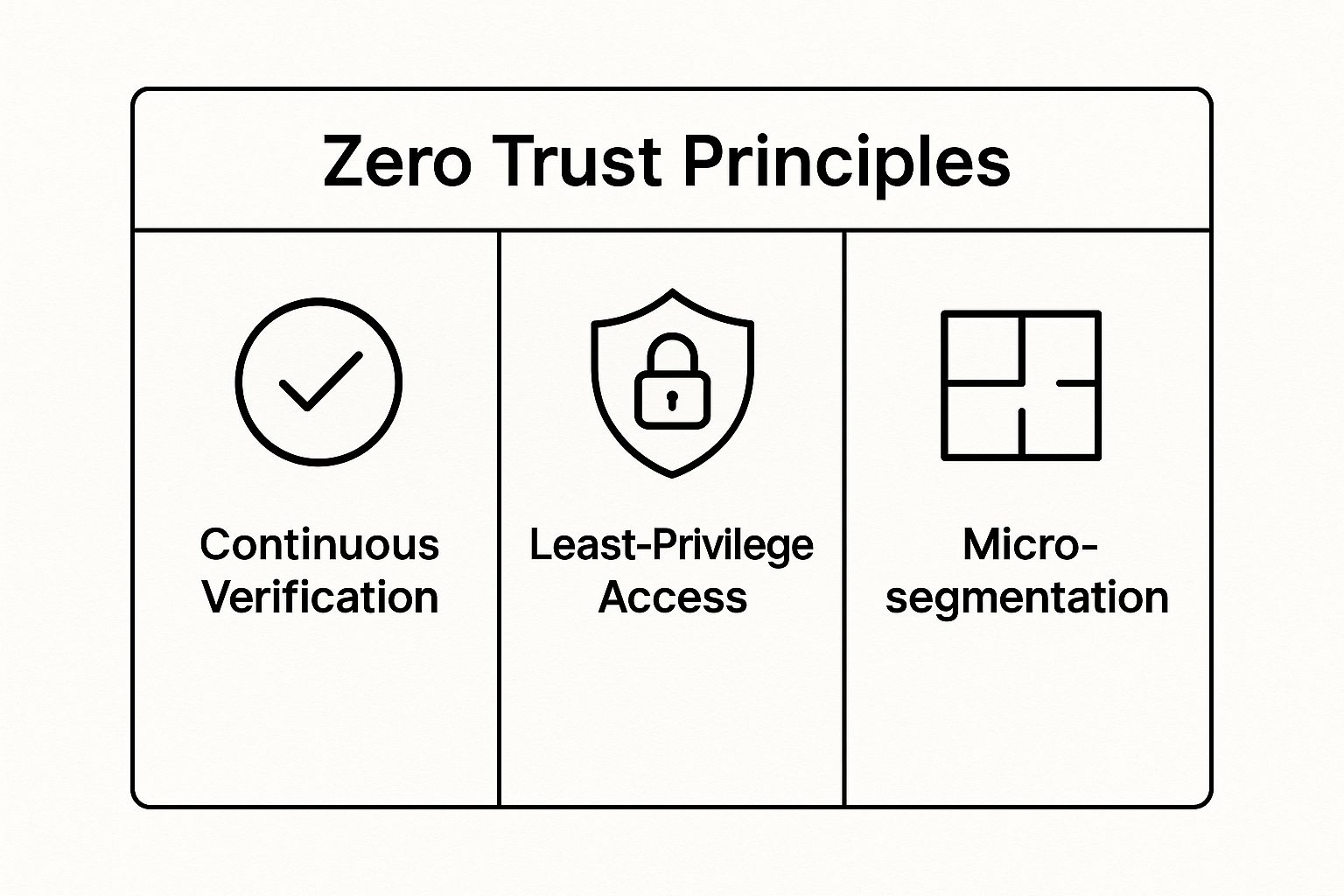
These three principles work together to create a robust, adaptable security framework that protects data no matter where your employees are located.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Getting started with Zero Trust doesn't require a complete overhaul overnight. You can begin by:
- Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA): This is the foundational layer, ensuring users are who they claim to be.
- Conducting an asset inventory: You can't protect what you don't know you have. Map out all users, devices, applications, and data.
- Starting a pilot program: Roll out Zero Trust policies to a small, low-risk group to identify and resolve challenges before a full-scale deployment.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Passwordless Solutions
Passwords alone are no longer a sufficient defense against modern cyber threats. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) strengthens security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to an account or application. This layered approach moves beyond what a user knows (a password) to include something they have (a hardware token or phone) or something they are (a fingerprint or face scan), dramatically reducing the risk of unauthorized access.

How It Strengthens Remote Work Security
Since password-related attacks account for the vast majority of data breaches, MFA is one of the most effective controls for securing a distributed workforce. It provides a critical safeguard against credential stuffing, phishing, and brute-force attacks. Even if a cybercriminal steals an employee's password, they cannot access the account without the additional verification factor.
The evolution of this technology is leading to passwordless solutions, which are even more secure and user-friendly. Companies like Microsoft have reported a 99.9% reduction in account compromise for users who enable MFA. This highlights its essential role in any robust remote work security best practices framework. By combining this strategy with other access controls, organizations can build a resilient defense. You can explore a deeper dive into modern access control in this guide on 2025 password management best practices.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Adopting MFA can be a seamless process with the right strategy. Start with these practical steps:
- Prioritize critical applications: Begin your MFA rollout by securing access to high-value systems first, such as your VPN, email platform, and core business applications.
- Favor app-based authenticators: When possible, guide users toward authenticator apps (like Google Authenticator or Duo Mobile) over SMS-based codes, which are more vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks.
- Implement risk-based authentication: Reduce user friction by configuring policies that only prompt for MFA during high-risk scenarios, such as when a user logs in from an unrecognized device or location.
- Train users on recovery: Ensure employees understand the account recovery procedures so they can regain access quickly and securely if they lose their primary authentication device.
3. Virtual Private Network (VPN) and Secure Remote Access
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a foundational technology for securing a remote workforce. It creates an encrypted, private tunnel over a public internet connection, essentially extending the corporate network to the employee's location. This secure channel protects sensitive data from being intercepted on untrusted networks, such as public Wi-Fi, and is a critical component of any robust remote work security best practices.
Modern VPN solutions have evolved beyond simple connections. They now offer cloud-based deployments for scalability, split-tunneling to optimize network traffic, and integration with Zero Trust frameworks. These features make VPNs a cornerstone of secure remote access, safeguarding against common threats like man-in-the-middle attacks.

How It Strengthens Remote Work Security
By encrypting all data transmitted between a remote employee and the company network, a VPN makes the information unreadable to anyone who might intercept it. This is essential for protecting intellectual property, customer data, and internal communications. Many organizations, from large enterprises like those using Cisco AnyConnect to growing businesses leveraging NordLayer, rely on VPNs to enforce a consistent security posture for all employees, regardless of location.
For companies looking to build a comprehensive security strategy, a VPN is the first line of defense. You can explore a detailed guide to learn more about implementing secure remote access for your team, which covers how to choose and configure the right tools. This technology ensures that even when employees are outside the traditional office perimeter, their connection to company resources remains private and protected.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Deploying a VPN effectively requires more than just choosing a provider. To maximize security and usability, follow these steps:
- Implement an "always-on" policy: Configure VPN clients on company-issued devices to connect automatically, ensuring employees are always protected without needing to take manual action.
- Use split-tunneling strategically: Route only company-related traffic through the VPN to conserve bandwidth and improve performance, while allowing general internet traffic to go through the user's local network.
- Choose providers with strict no-logs policies: Select a VPN service that does not store user activity logs, adding an extra layer of privacy and security.
- Provide clear setup guides and support: Ensure employees can easily install and troubleshoot the VPN client to minimize downtime and encourage adoption.
4. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions
Traditional antivirus software is no longer sufficient to protect the modern remote workforce. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions offer a more advanced, comprehensive approach to security, providing continuous monitoring, threat detection, and automated response capabilities for every device connecting to your network, including laptops, desktops, and mobile phones.
How It Strengthens Remote Work Security
EDR systems operate on the assumption that endpoints, especially those used remotely, are prime targets for sophisticated attacks. They use behavioral analysis and machine learning to identify anomalous activities that signature-based antivirus tools would miss. This is a critical component of any modern remote work security best practices, as it provides visibility into devices operating outside the traditional network perimeter.
Leading companies have demonstrated the power of EDR. CrowdStrike’s Falcon platform protects millions of endpoints globally with its cloud-native architecture, while SentinelOne’s AI-powered solution has been successfully deployed by organizations like JetBlue and Aston Martin to automate threat response. These examples highlight EDR's effectiveness in securing distributed environments against advanced threats.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Deploying an EDR solution requires more than just installation. To maximize its effectiveness, you should:
- Establish a behavioral baseline: Allow the EDR tool to learn normal user and device activity before fully activating its alerting and response features. This helps reduce the number of false positives.
- Integrate with your SIEM: Feed EDR data into your Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system for centralized logging and a holistic view of your security posture.
- Develop incident response playbooks: Create clear, step-by-step guides for your security team to follow when the EDR detects common threats, ensuring a swift and consistent response.
- Implement automated responses: Configure the EDR to automatically quarantine infected devices or block malicious processes when it detects known, high-confidence threat patterns.
5. Secure Cloud Storage and Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
With data no longer confined to on-premise servers, securing information in the cloud is paramount. Combining secure cloud storage with Data Loss Prevention (DLP) creates a powerful defense for sensitive information. This dual approach ensures data is encrypted and protected wherever it is stored, accessed, or shared, addressing the unique risks of a distributed workforce.
How It Strengthens Remote Work Security
DLP solutions act as a digital gatekeeper, actively monitoring, detecting, and blocking the unauthorized transmission of confidential data. When an employee tries to send a sensitive file to a personal email or an unsanctioned cloud app, DLP policies can intervene. This strategy is critical for preventing both accidental and malicious data leaks, a common challenge in remote settings.
Leading platforms like Microsoft Purview DLP and Forcepoint are widely used to safeguard data across Office 365, endpoints, and cloud applications. For instance, a financial institution might use Forcepoint to prevent client financial data from being copied to a USB drive, while a healthcare organization uses Symantec DLP to block the sharing of Protected Health Information (PHI) via unauthorized channels. This makes DLP an essential component of modern remote work security best practices.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Integrating DLP and secure cloud storage requires a strategic, phased approach to avoid disrupting workflows. You can get started by:
- Beginning in discovery mode: First, deploy DLP in a monitor-only mode to understand how sensitive data flows through your organization without blocking any actions.
- Focusing on high-priority data: Start by creating policies to protect your most critical assets, such as intellectual property or customer PII, to reduce false positives and alert fatigue.
- Implementing graduated responses: Configure policies to first warn users of potential violations, then escalate to blocking actions or encrypting data for repeat or high-risk offenses. This helps train employees on correct data handling procedures.
6. Security Awareness Training and Phishing Simulation
Even the most advanced security tools can be bypassed if an employee is tricked into giving away their credentials. Security awareness training moves beyond technology to fortify the "human firewall" by educating employees on current threats and best practices. This is paired with phishing simulations, which are controlled, harmless cyber attack drills designed to test and reinforce that training.
How It Strengthens Remote Work Security
This human-centric approach is vital because remote workers are prime targets for social engineering attacks, operating outside the physical oversight of an office. Regular training and simulation build a culture of security vigilance, transforming employees from potential liabilities into the first line of defense. By conditioning staff to recognize and report suspicious activity, organizations can dramatically reduce the risk posed by phishing, which is the starting point for the vast majority of cyber incidents.
Industry leaders like KnowBe4, which serves over 50,000 organizations, and Proofpoint have built entire platforms around this principle. Microsoft's own internal security training, for instance, successfully reduced employee susceptibility to phishing by over 60%, demonstrating the direct impact of these programs on an organization’s security posture. For any company serious about remote work security best practices, empowering employees with knowledge is a non-negotiable step.
Actionable Implementation Tips
An effective training program is continuous, not a one-time event. You can build a robust program by:
- Customizing content: Make training relevant to specific job roles and the actual threats employees are likely to face.
- Varying simulation difficulty: Start with basic phishing emails and gradually increase the sophistication to mimic real-world attack evolution.
- Providing immediate feedback: When an employee clicks a simulated phishing link, provide instant, non-punitive educational feedback explaining the red flags they missed.
- Tracking meaningful metrics: Go beyond simple click rates. Measure reporting rates, time to report, and overall improvement to gauge program effectiveness.
7. Device Management and Mobile Device Management (MDM)
With employees accessing company data from a wide range of personal and corporate-owned devices, maintaining security standards across all endpoints is a major challenge. Device Management and Mobile Device Management (MDM) platforms provide a centralized solution, giving IT teams the power to enforce security policies, manage applications, and monitor the health of every device connecting to the network. This approach ensures that laptops, smartphones, and tablets meet security baselines before they can access sensitive resources.
How It Strengthens Remote Work Security
MDM solutions create a unified security posture for your distributed fleet of devices. Instead of manually configuring each machine, IT can push updates, install required security software, and even remotely wipe a device if it is lost or stolen. This capability is critical for containing potential breaches and ensuring that all endpoints adhere to corporate compliance standards. It also ties directly into broader security strategies, such as managing user access controls, which you can explore further in guides on how user permissions management boosts security.
Industry leaders like Microsoft Intune and VMware Workspace ONE demonstrate the scalability of MDM, managing millions of devices for global enterprises. These platforms are essential for any organization looking to implement robust remote work security best practices, as they provide critical visibility and control over a complex and ever-changing device landscape.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Adopting an MDM solution can be a smooth process with proper planning. Here are a few key steps to get started:
- Establish a clear BYOD policy: Before enrolling devices, define what is and isn’t acceptable for personal devices accessing company data. This policy should cover security requirements, privacy expectations, and user responsibilities.
- Use conditional access policies: Configure rules that grant or deny access to corporate resources based on device compliance. For example, block access from devices that are jailbroken or missing critical security patches.
- Implement a graduated response system: Instead of immediately blocking a non-compliant device, start with automated notifications. Escalate to restricted access and, finally, a full block if the issue remains unresolved.
8. Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Management
A "set it and forget it" approach to security is a recipe for disaster, especially with a distributed workforce. Regular security audits and proactive vulnerability management form a continuous cycle of assessment and improvement. This practice involves systematically examining your remote work security posture to identify weaknesses, prioritize threats, and implement timely remediation strategies.
How It Strengthens Remote Work Security
In a remote setting, the attack surface expands exponentially with every employee's home network, personal device, and cloud service. A proactive auditing and vulnerability management program helps you stay ahead of threats by systematically uncovering and closing these security gaps before they can be exploited. It moves security from a reactive, incident-driven model to a proactive, risk-based one.
Leading vulnerability management platforms like Qualys VMDR and Rapid7 InsightVM provide organizations with comprehensive visibility across their distributed environments. These tools automate the process of scanning for vulnerabilities, analyzing their potential impact, and prioritizing patches. This continuous monitoring is a cornerstone of effective remote work security best practices, ensuring that your defenses adapt as new threats emerge.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Implementing a robust audit and vulnerability management program is a critical step. You can begin by:
- Establishing a regular audit schedule: Create a calendar for different types of assessments (e.g., quarterly vulnerability scans, annual penetration tests) based on risk levels.
- Prioritizing vulnerabilities: Use a risk-based approach, focusing on vulnerabilities with known exploits that affect critical systems accessible to remote workers. The CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) is the industry standard for this.
- Integrating vulnerability and patch management: Ensure that your scanning tools and patching systems are linked. This creates an efficient workflow from identifying a vulnerability to deploying the fix.
- Using a combination of tools: Combine automated scanners like Tenable Nessus with manual penetration testing and bug bounty programs to uncover a wider range of security flaws.
8 Key Remote Work Security Practices Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Trust Security Architecture | High complexity; requires cultural shift 🔄🔄 | Significant investment in technology & training ⚡ | Strong attack surface reduction; detailed visibility 📊📊 | Organizations needing strong adaptive security & cloud/hybrid environments 💡 | Continuous verification, least-privilege access, segmentation ⭐⭐ |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Moderate complexity; managing multiple methods 🔄 | Moderate to high (hardware tokens, training) ⚡ | 99.9% reduction in account compromises 📊⭐ | Securing user authentication and compliance; all device types 💡 | Phishing defense, passwordless options, audit trails ⭐ |
| Virtual Private Network (VPN) | Moderate; configuration complexity and maintenance 🔄 | Moderate infrastructure and support ⚡ | Encrypted remote access; location masking 📊 | Secure remote connectivity over untrusted networks 💡 | Strong data encryption, scalable, cost-effective ⭐ |
| Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) | High; requires skilled analysts and tuning 🔄🔄 | High cost and skilled security team ⚡ | Detects advanced threats, reduces breach costs 📊⭐ | Monitoring and protecting endpoints outside perimeter 💡 | Real-time monitoring, rapid response, threat hunting ⭐⭐ |
| Secure Cloud Storage and DLP | Moderate to high; complex policy and tuning 🔄 | High storage and processing overhead ⚡ | Prevents data leaks; compliance and visibility 📊 | Protecting sensitive data in cloud and remote environments 💡 | Encryption, automated blocking, centralized visibility ⭐ |
| Security Awareness Training & Phishing | Low to moderate; ongoing management 🔄 | Low to moderate investment ⚡ | 70% fewer security incidents through training 📊⭐ | Addressing human element in cybersecurity for remote workers 💡 | Behavior change, metrics, cost-effective ⭐ |
| Device Management and Mobile Device Mgmt | Moderate to high; diverse device management 🔄 | Moderate to high licensing and administration ⚡ | Consistent device security; rapid incident response 📊 | Managing security policies across diverse remote devices 💡 | Remote control, compliance monitoring, BYOD support ⭐ |
| Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Mgmt | High; time-consuming and resource intensive 🔄🔄 | High cost and skilled professionals ⚡ | 95% fewer security incidents; proactive risk reduction 📊⭐ | Continuous security posture assessment across distributed environments 💡 | Risk prioritization, compliance, continuous improvement ⭐ |
Building a Culture of Continuous Security
The transition to a remote or hybrid work model is no longer a temporary shift; it is a permanent evolution of the modern workplace. Navigating this new landscape successfully requires more than just providing employees with laptops and internet access. It demands a fundamental rethinking of how we approach security, transforming it from a static checklist into a dynamic, living culture. The remote work security best practices detailed throughout this guide are not isolated solutions but interconnected components of a comprehensive defense strategy.
By implementing a Zero Trust architecture, you lay a foundation of "never trust, always verify," which is essential when the traditional network perimeter has dissolved. Layering on robust Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and exploring passwordless solutions hardens access controls at the individual level, dramatically reducing the risk of credential theft. Meanwhile, mandating the use of a secure corporate VPN and deploying advanced Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions ensures that both data in transit and the devices accessing it are protected from sophisticated threats.
From Policy to Practice: Activating Your Security Strategy
Theoretical knowledge is only valuable when put into practice. The real test of your security posture lies in its daily application. This is where continuous effort becomes critical.
- Empower Your People: Consistent security awareness training and realistic phishing simulations are your first line of defense. An educated workforce that can identify and report suspicious activity is an invaluable asset.
- Maintain Control: Robust device management policies, including Mobile Device Management (MDM), provide the necessary oversight to enforce security standards on all endpoints, whether company-owned or personal.
- Stay Proactive, Not Reactive: Regular security audits and a structured vulnerability management program are non-negotiable. They allow you to identify and remediate weaknesses before malicious actors can exploit them, shifting your team from a constant state of reaction to one of proactive defense.
Ultimately, mastering these remote work security best practices is about building resilience. It’s about creating an environment where your team can collaborate, innovate, and thrive from anywhere in the world, backed by a security framework that is as flexible and dynamic as they are. This proactive, multi-layered approach doesn't just prevent data breaches; it builds trust with your clients, protects your reputation, and enables sustainable growth in a distributed world. Fostering a culture where every team member feels a sense of ownership over security is the ultimate goal, turning a potential vulnerability into your greatest strength.
Ready to simplify and secure how your team shares access to essential software and subscriptions? AccountShare provides a centralized platform to manage shared accounts with customizable permissions and secure credential handling, perfectly complementing your remote work security best practices. Explore how AccountShare can streamline collaboration without compromising security.
