
Reduce Software Costs: Top Strategies for 2025
Share
Trimming Your Tech Budget: Taking Control of Software Costs
Software expenses adding up? This listicle provides seven actionable strategies to reduce software costs without compromising functionality. Learn how to maximize your software ROI by exploring open source alternatives, optimizing software licenses, migrating to the cloud, standardizing software choices, rationalizing your software portfolio, negotiating better contracts, and considering custom development. These cost-saving measures can free up resources for other important initiatives, putting you back in control of your tech budget.
1. Open Source Software Adoption
One of the most effective ways to reduce software costs is by adopting open source alternatives to proprietary software. This approach leverages software that is freely available for use, modification, and distribution, offering a cost-effective solution for organizations and individuals seeking to minimize software expenses without sacrificing functionality. Open source software provides a wide range of options for almost every proprietary solution, from operating systems and office suites to databases and web browsers. This makes it a powerful tool for anyone looking to reduce software costs.
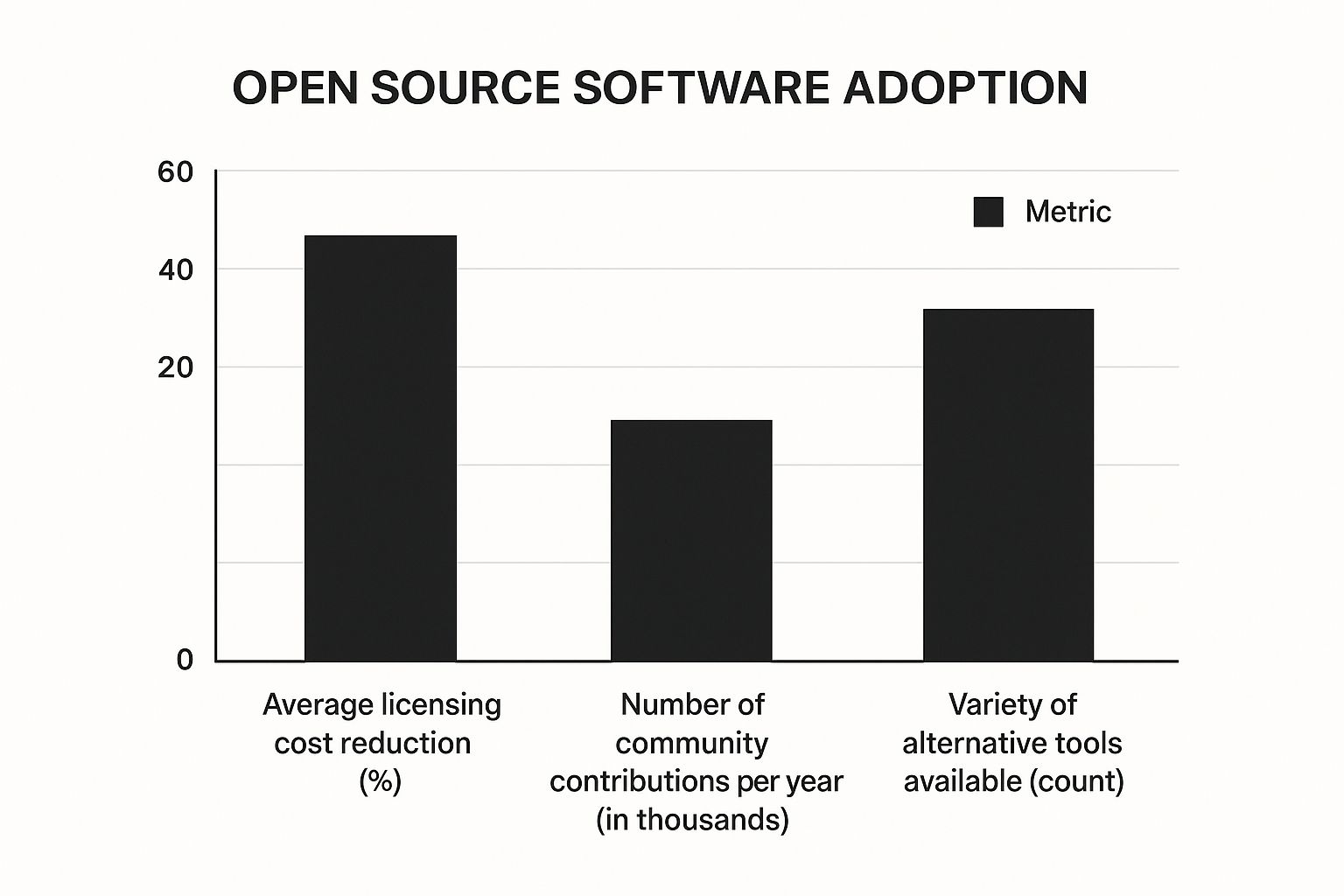
Open source software offers several key features including free or low-cost licenses for commercial-grade software, community-driven development and support, and the flexibility to modify the source code. This allows users to tailor the software to their specific needs, a level of customization rarely available with proprietary solutions.
The infographic below visualizes data comparing the total cost of ownership (TCO) of open source and proprietary software solutions over a five-year period.

As the infographic illustrates, while initial setup costs for open source software might be slightly higher due to potential integration needs or specialized skills required, the overall TCO is significantly lower over time compared to proprietary software. This is primarily driven by the elimination of recurring licensing fees and reduced vendor lock-in. For example, the chart shows that while proprietary software costs accrue steadily due to ongoing license fees, the cost curve for open source software flattens considerably after the initial investment.
Pros of Open Source Software Adoption:
- Eliminates or reduces licensing fees: This is the most significant advantage, directly contributing to reducing software costs.
- No vendor lock-in: Users are free to switch providers or even maintain the software themselves.
- Strong security: Community review often leads to quicker identification and resolution of security vulnerabilities.
- Continuous improvements: A global developer community contributes to ongoing feature enhancements and bug fixes.
Cons of Open Source Software Adoption:
- May require specialized technical skills: Implementing and maintaining some open source solutions may require specialized expertise.
- Community-based support: Support is typically provided through community forums, which might not offer the same level of responsiveness as dedicated support teams.
- Potential integration challenges: Integrating open source software with existing proprietary systems can sometimes be complex.
- Some enterprise features may be less polished: Certain advanced features found in commercial alternatives might be less developed in open source options.
Examples of Successful Open Source Software Adoption:
- Mozilla Firefox replacing Internet Explorer: A popular open-source web browser alternative.
- Linux operating systems replacing Windows Server: A cost-effective solution for server infrastructure.
- LibreOffice instead of Microsoft Office: A free and open-source office suite comparable to Microsoft Office.
- MySQL or PostgreSQL instead of Oracle Database: Robust and scalable open-source database management systems.
Tips for Successful Open Source Software Adoption:
- Start with non-critical systems: Gain experience with open source software by implementing it in less critical areas first.
- Build internal expertise: Invest in training to develop the necessary skills for managing open source solutions.
- Consider paid support options: Companies like Red Hat and Canonical offer paid support for enterprise deployments.
- Calculate total cost of ownership: Don't just focus on license savings; consider all associated costs, including implementation, maintenance, and support.
Popularized By:
Organizations like the Linux Foundation, Apache Software Foundation, Mozilla Foundation, and Red Hat have played a key role in popularizing and advancing open source software.
By carefully considering the pros, cons, and implementation tips, individuals and organizations can leverage open source software to significantly reduce software costs without compromising on quality or functionality. This makes open source adoption a crucial strategy for anyone looking to optimize their software budget.
2. Software License Optimization
Software license optimization is a crucial strategy for any organization looking to reduce software costs. It involves a systematic approach to auditing, managing, and optimizing your software licenses to ensure you're neither overspending on unused licenses nor risking costly compliance penalties due to under-licensing. This process helps you gain full visibility into your software assets and how they're being utilized, allowing you to make informed decisions about purchasing and deployment.
This method works by first gaining a clear understanding of your current license inventory. This involves identifying all the software deployed within your organization, the types of licenses you own, and their respective usage metrics. License inventory and tracking systems are essential tools in this phase. Then, by leveraging usage monitoring tools, you can analyze how often and by whom specific software is being used. This data informs decisions about license harvesting from inactive users, allowing you to reclaim and reassign underutilized licenses. Finally, armed with a comprehensive understanding of your software usage, you are in a stronger position to negotiate better contract terms with vendors and explore options like enterprise agreements for widely-used software.
The benefits of software license optimization are significant. It directly reduces unnecessary license purchases, a common source of wasted IT budget. It also helps avoid costly compliance penalties, which can be substantial depending on the vendor and the extent of the violation. Furthermore, the insights gained through this process provide invaluable visibility into software asset utilization, enabling more strategic IT planning. This data also creates leverage for vendor negotiations, empowering organizations to secure better pricing and contract terms.
For example, Microsoft reportedly saved $181 million annually by implementing Software Asset Management (SAM) tools. Similarly, Pfizer optimized its Adobe Creative Cloud licenses, and IBM has helped major banks consolidate their software licenses, leading to significant cost savings. Oracle license optimization at Cerner also resulted in a reported 30% cost reduction. These real-world examples highlight the potential for substantial savings through effective software license optimization.
However, it's important to be aware of the potential challenges. Software license optimization requires ongoing management and monitoring. The initial implementation can be time-consuming, especially for organizations with complex IT environments. It may also require specialized software asset management tools, like Flexera or Snow Software, which can add to the initial investment. Finally, reclaiming and reassigning underused software can sometimes create internal resistance, requiring careful change management.
Actionable Tips for Software License Optimization:
- Conduct regular software audits: Regularly audit your software inventory to identify unused or underutilized licenses.
- Centralize purchasing decisions: Centralized purchasing allows for better negotiation and control over software licenses.
- Implement automated usage tracking: Automated tools provide real-time data on software usage, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Consider specialized software asset management tools: Tools like Flexera or Snow Software offer advanced features for license management and optimization.
- Negotiate enterprise agreements for widely-used software: Enterprise agreements can provide cost savings and simplify license management for frequently used applications.
Software license optimization deserves its place on this list because it addresses a common area of overspending in IT budgets. It's a proactive approach that not only reduces costs but also strengthens an organization's overall software asset management practices. For organizations of all sizes, especially those with complex software deployments, implementing a robust software license optimization strategy is critical for achieving long-term cost savings and ensuring compliance. Learn more about Software License Optimization This approach is particularly relevant to our target audience, which includes tech-savvy individuals, families, small businesses, students, and digital nomads, all of whom can benefit from optimizing their software spending. Companies like Gartner, Flexera, Snow Software, and ServiceNow have all popularized the importance and benefits of Software Asset Management and License Optimization. By taking control of your software licenses, you can free up resources for other critical initiatives and improve your bottom line.
3. Cloud Migration & SaaS Adoption
One of the most effective ways to reduce software costs is by transitioning from traditional on-premises software to cloud-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models. This approach replaces the large upfront costs and ongoing maintenance expenses of owning and operating software with a subscription-based model, effectively shifting capital expenditure (CAPEX) to operational expenditure (OPEX). Instead of purchasing software licenses and the necessary hardware to run them, businesses and individuals pay a recurring fee to access software hosted and managed by a third-party provider. This shift provides significant cost savings and operational efficiencies.

SaaS solutions often utilize pay-as-you-go pricing models, allowing you to scale your usage up or down based on your actual needs. Automatic updates and maintenance are handled by the provider, eliminating the need for internal IT resources and ensuring you always have access to the latest features and security patches. This method offers significant advantages for reducing software costs due to reduced hardware requirements, pay-as-you-go pricing, and automatic updates.
Several successful implementations demonstrate the cost-saving potential of SaaS. Adobe's shift from the Creative Suite to the Creative Cloud subscription model allows users access to the latest software versions for a monthly fee, eliminating the need for costly upgrades. Similarly, Microsoft's Office 365 provides access to the entire Office suite and cloud storage for a fraction of the cost of traditional perpetual licenses. Salesforce's cloud-based CRM system has revolutionized customer relationship management by offering a scalable and affordable alternative to on-premises solutions. Even simple file storage has seen a shift with services like Dropbox Business replacing expensive and difficult-to-maintain file servers.
Here are some actionable tips for successful cloud migration and SaaS adoption:
- Start small: Begin by migrating non-critical applications to the cloud to gain experience and minimize potential disruption.
- Implement strict cloud governance and monitoring: Track cloud spending closely to avoid unexpected cost overruns. Utilize cloud management platforms to monitor resource usage and optimize spending.
- Negotiate multi-year contracts: For stable workloads, negotiating multi-year contracts with SaaS providers can often secure significant discounts.
- Utilize reserved instances or committed use discounts: If your workload is predictable, explore reserved instances or committed use discounts offered by cloud providers to reduce costs.
- Right-size cloud resources: Regularly review your cloud resource allocation and adjust based on actual usage to avoid paying for unused capacity.
This approach is particularly beneficial for tech-savvy individuals seeking access to premium software without the hefty price tag, families wanting to share streaming and gaming accounts securely and affordably, small businesses needing collaborative tools at a lower cost, students looking for affordable subscription options, and digital nomads requiring efficient account management solutions across multiple devices.
Pros of Cloud Migration & SaaS Adoption:
- Eliminates upfront hardware costs
- Reduces IT maintenance staff requirements
- Provides flexible scaling options
- Enables remote work capabilities
- Updates and security patches are managed by the provider
Cons of Cloud Migration & SaaS Adoption:
- Potential for cost creep if usage is not monitored
- Data security and compliance considerations
- Possible performance issues depending on internet connectivity
- Long-term subscription costs may exceed one-time purchases in some cases
Cloud migration and SaaS adoption deserves a prominent place on this list because it offers a compelling combination of cost savings, flexibility, and operational efficiency. By leveraging the power of the cloud, businesses and individuals can significantly reduce their software costs while simultaneously gaining access to cutting-edge technology and simplified IT management. Popularized by industry giants like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and Salesforce, the SaaS model has become a dominant force in the software industry and offers a powerful solution for reducing software expenses.
4. Software Standardization
Software standardization is a powerful strategy to reduce software costs by streamlining the variety of applications used across an organization. This involves consolidating the software portfolio and establishing enterprise-wide standards for specific functions, like communication, project management, or design. By reducing the number of different software licenses your organization needs, you can unlock substantial savings through bulk purchasing, simplified IT support, and more efficient training programs. This approach is particularly effective for reducing recurring software expenses, a key concern for cost-conscious individuals, families, small businesses, and large enterprises alike.
How it Works:
Software standardization works by identifying overlapping functionalities in the existing software ecosystem and selecting a single, preferred application to fulfill those needs across different departments or teams. This often involves consolidating multiple point solutions into a single platform with broader capabilities. For example, instead of using several different project management tools, a company might standardize on one platform for all project-related activities. This centralized procurement and management approach simplifies licensing, upgrades, and maintenance. It also streamlines support processes, as IT teams only need to be proficient in a smaller number of applications.
Features and Benefits:
- Reduced software portfolio diversity: A smaller, more manageable software portfolio.
- Enterprise-wide standard applications: Consistent tools and workflows across teams.
- Centralized procurement and management: Simplified licensing and purchasing.
- Streamlined support processes: Easier troubleshooting and user assistance.
- Better interoperability between systems: Improved data sharing and collaboration.
- Stronger negotiating position with vendors: Leverage bulk purchases for better pricing.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Volume discounts through consolidated purchasing: Negotiate lower prices per license.
- Reduced training costs: Fewer applications mean fewer training programs.
- Simplified IT support requirements: Streamlined troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Better interoperability between systems: Enhanced data flow and collaboration.
Cons:
- May not meet specialized departmental needs: Some departments might require specific features not available in the standardized software.
- Potential user resistance to change: Employees accustomed to specific tools might resist transitioning to new ones.
- Initial migration costs: Data migration and system integration can incur upfront expenses.
- Possible reduced innovation from standardization: Limiting software choices might restrict access to cutting-edge features found in niche applications.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several large organizations have successfully implemented software standardization initiatives to reduce software costs and improve efficiency. Examples include:
- General Electric: Standardized on the Microsoft productivity suite across 300,000 employees.
- Boeing: Standardized CAD software across engineering teams.
- Bank of America: Reduced its application portfolio from 16,000 to 5,000 applications.
- Procter & Gamble: Standardized ERP systems globally.
Tips for Implementation:
- Conduct thorough needs assessment across departments: Understand the specific requirements of different teams before selecting standardized software.
- Create clear exception processes for specialized needs: Accommodate departments with unique requirements that cannot be met by the standard software.
- Phase implementation to manage change resistance: Gradually roll out the standardized software to minimize disruption and allow employees to adapt.
- Focus first on high-cost, widely-used application categories: Prioritize standardization efforts on applications with the greatest potential for cost savings.
- Involve end-users in standardization decisions: Gather feedback from employees to ensure the chosen software meets their needs and promotes adoption.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Software standardization is a valuable strategy when an organization aims to reduce recurring software costs, simplify IT management, and improve collaboration. It's particularly beneficial for organizations with a large number of employees or diverse software portfolios. Learn more about Software Standardization
This method deserves its place on this list because it offers a practical and proven approach to reducing software expenses while improving operational efficiency. It's a valuable consideration for anyone looking to optimize their software spending, from tech-savvy individuals and families to small businesses and large corporations. Popularized by leading consulting firms like Deloitte Consulting, McKinsey & Company, Gartner, and KPMG, software standardization is a widely recognized best practice for cost optimization.
5. Software Rationalization
Software rationalization is a key strategy to reduce software costs and streamline your IT landscape. It involves systematically evaluating your entire software portfolio to identify and eliminate redundancies, underutilized applications, and outdated systems. This process allows organizations to optimize their spending, improve security, and simplify IT management. By consolidating similar tools and retiring unnecessary software, businesses can free up valuable resources and focus on strategic initiatives.
This approach goes beyond simply cutting costs; it's about making informed decisions about which applications truly deliver value to the organization. The process typically involves conducting a thorough application portfolio assessment, analyzing software usage metrics, and developing a retirement plan for legacy systems, all while considering the potential business impact. Features like redundancy identification and business impact evaluation ensure that the rationalization process is strategic and minimizes disruption.
Software rationalization deserves its place on this list because it addresses a common problem in many organizations: software bloat. Often, companies accumulate numerous applications over time, many of which perform similar functions or become obsolete. This leads to unnecessary spending on licenses, maintenance, and infrastructure. Rationalization tackles this issue head-on, offering a structured approach to reduce software costs significantly.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Johnson & Johnson: Reduced its application count by 30% through a comprehensive rationalization effort.
- Wells Fargo: Consolidated more than 5,000 applications to less than 3,000, streamlining their IT environment.
- General Motors: Achieved $1 billion in IT savings through application rationalization.
- AstraZeneca: Reduced IT costs by 25% through a strategic rationalization initiative.
These examples demonstrate the significant cost savings and efficiency gains that can be achieved through software rationalization.
Pros:
- Eliminates maintenance costs for unnecessary applications.
- Reduces complexity of the IT landscape.
- Improves security by removing outdated and vulnerable software.
- Decreases infrastructure requirements, leading to further cost savings.
- Simplifies compliance management.
Cons:
- Requires significant initial analysis and planning.
- May face resistance from application owners or departments.
- Risk of disrupting business processes if not carefully managed.
- Potential data migration challenges when consolidating applications.
- May require substantial change management to ensure user adoption.
Actionable Tips for Reducing Software Costs Through Rationalization:
- Create a comprehensive application inventory: Document all software used within the organization, including details like licensing costs, usage metrics, and business purpose.
- Develop clear evaluation criteria: Establish objective criteria for deciding which applications to retire, consolidate, or retain.
- Establish governance: Implement a governance framework to prevent future application sprawl and ensure ongoing optimization.
- Prioritize high-cost/low-value applications: Focus on eliminating applications that generate minimal business value but incur significant costs.
- Implement phased retirement: Minimize disruption by retiring applications in phases, allowing time for user training and adjustment.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Software rationalization is particularly beneficial for organizations experiencing rapid growth, mergers and acquisitions, or those with a complex and sprawling IT environment. It's also a valuable strategy for companies looking to reduce IT costs, improve security, and simplify operations. If your organization struggles with managing numerous software licenses, experiences redundant applications, or seeks to optimize its IT spending, software rationalization is a crucial step to consider. This approach provides a structured framework to achieve significant cost savings and improve overall IT efficiency. Popularized by consulting giants like Boston Consulting Group, Capgemini, Accenture, and Ernst & Young, software rationalization is a proven method for streamlining IT and achieving significant ROI.
6. Vendor Negotiation & Contract Management
One of the most effective ways to reduce software costs is through strategic vendor negotiation and ongoing contract management. This approach focuses on leveraging market competition, timing, and negotiation tactics to secure the best possible deals and optimize your software spending. It deserves a place on this list because it can yield significant savings – often between 10-30% – and goes beyond simple price reductions to improve contract terms and create more flexible usage rights.
How it Works:
Vendor negotiation and contract management involves a thorough understanding of your software needs, the competitive landscape, and the terms of your existing agreements. It’s about proactively engaging with vendors to negotiate better pricing, favorable terms, and optimized agreement structures. This can include everything from competitive bidding processes and volume-based discounts to negotiating lower maintenance costs and consolidating multiple contracts.
Features and Benefits:
- Competitive vendor bidding processes: Pitting vendors against each other encourages them to offer their best possible price and terms.
- Contract term optimization: Negotiating favorable contract lengths and renewal options can prevent automatic price increases and lock in better rates.
- Volume-based discount structures: Leveraging your organization's size and purchasing power to secure discounts based on the number of licenses or users.
- Maintenance cost reduction: Negotiating lower maintenance fees or decoupling them from software licenses can result in significant savings.
- Enterprise agreement consolidation: Combining multiple contracts with a single vendor can streamline management and unlock volume discounts.
These features translate into tangible benefits, including a significant reduction in software costs, improved contract terms beyond just price, more flexible usage rights, stronger vendor relationships, and reduced compliance risks.
Examples of Success:
Major corporations have demonstrated the power of vendor negotiation and contract management. Cisco reportedly saved $500 million through renegotiating their Oracle contract. Novartis reduced Microsoft licensing costs by 22%, while the Royal Bank of Scotland consolidated IBM contracts for 15% savings. Even Home Depot leveraged competition between SAP vendors to reduce their costs by 18%.
Actionable Tips for Reducing Software Costs:
- Plan ahead: Start negotiations 6-9 months before renewal dates to allow ample time for research and discussion.
- Research the market: Understand market rates and competitor pricing to strengthen your negotiating position.
- Consider expert help: Bringing in specialized IT procurement consultants can provide valuable expertise and leverage.
- Consolidate purchases: Bundle software purchases to qualify for volume discounts and simplify contract management.
- Understand your usage: Analyze your actual software usage to avoid paying for licenses you don't need.
- Be prepared to switch: Maintaining the willingness to switch vendors gives you significant leverage during negotiations.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Can achieve 10-30% savings on software costs
- Improves contract terms beyond just price
- Creates more flexible usage rights
- Establishes better vendor relationships
- Reduces compliance risks
Cons:
- Requires specialized negotiation expertise
- Time-consuming process
- May involve difficult conversations with vendors
- Contract complexity can increase
- Savings may diminish over multiple renewal cycles
When and Why to Use This Approach:
This approach is particularly valuable for organizations with significant software expenditures, complex licensing agreements, or upcoming contract renewals. It’s also beneficial for those seeking to optimize their software usage and improve their overall vendor relationships. For further insights, you can learn more about Vendor Negotiation & Contract Management. Whether you're a tech-savvy individual, a family sharing accounts, a small business, a student, or a digital nomad, effective vendor negotiation can contribute significantly to reducing software costs and maximizing your budget.
7. Custom Software Development
When aiming to reduce software costs, custom software development often emerges as a surprisingly effective long-term strategy, particularly for organizations with unique or complex needs. Instead of relying on expensive off-the-shelf software that may include unnecessary features or force you to adapt your processes to the software's limitations, custom development allows you to build precisely what you need, ultimately reducing software costs in the long run. This approach involves designing, coding, and deploying software tailored to specific organizational requirements.
How it Works:
Custom software development involves a systematic process: starting with a thorough requirements analysis to define the exact functionalities needed. This is followed by the design and development phase, where the software is built, tested, and deployed. Finally, ongoing maintenance and updates ensure the software continues to perform optimally and adapt to evolving business needs. You have several options for development methodologies, including in-house development, outsourcing to a third-party vendor, or a hybrid approach combining both.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several high-profile companies demonstrate the power of custom software development to achieve specific business objectives and reduce software costs over time. Netflix, for example, developed its own custom content delivery system to handle its massive streaming volume more efficiently than off-the-shelf solutions. Similarly, Goldman Sachs built proprietary trading platforms to gain a competitive edge, and Walmart created custom inventory management systems optimized for its complex logistical needs. Even Uber relies on custom dispatch and mapping software tailored to the specifics of its ride-hailing service. These examples highlight how custom software can address very specific needs and provide significant long-term cost savings compared to licensing numerous commercial products or adapting to ill-fitting software.
Actionable Tips for Reducing Software Costs with Custom Development:
- Start with Detailed Requirements Analysis: Clearly defining your needs is crucial for a successful custom software project. This minimizes scope creep and ensures the final product meets your exact specifications.
- Consider Agile Development Methodologies: Agile allows for iterative development and faster adaptation to changing requirements, reducing the risk of costly rework.
- Evaluate Build vs. Buy with Comprehensive TCO Analysis: Conduct a thorough Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis to compare the long-term costs of custom development against purchasing commercial software. Factor in licensing fees, implementation costs, maintenance, and potential productivity gains.
- Consider Offshore or Nearshore Development to Reduce Costs: Explore leveraging development teams in lower-cost regions while ensuring proper communication and project management.
- Plan for Long-Term Maintenance From the Beginning: Allocate budget and resources for ongoing maintenance, updates, and potential future enhancements.
- Implement Proper Documentation and Knowledge Transfer: Ensure thorough documentation of the codebase and processes for easier maintenance and future development.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Eliminates Ongoing Licensing Fees: No more recurring subscription costs.
- Provides Exactly the Features Needed Without Bloat: Streamlined functionality focused on your requirements.
- Offers Competitive Advantage Through Unique Capabilities: Develop unique solutions that differentiate your business.
- Adapts Precisely to Business Processes: Software designed around your workflow, not the other way around.
- Enables Rapid Iteration and Improvements: Greater control over updates and enhancements.
Cons:
- Higher Upfront Development Costs: Initial investment can be significant.
- Requires Ongoing Maintenance and Updates: Budget for continuous improvement and bug fixes.
- Development Risks Including Delays and Budget Overruns: Careful planning and project management are essential.
- Potential Challenges Finding Specialized Talent: Securing skilled developers can be competitive.
- May Lack the Polish of Commercial Solutions: User interface and experience may require extra attention.
Why Custom Software Development Deserves its Place in the List:
Custom software development offers a pathway to significant long-term cost reduction by eliminating licensing fees and maximizing efficiency. While the initial investment may seem daunting, a comprehensive TCO analysis often reveals that custom development is more cost-effective in the long run, especially for organizations with specialized needs. It empowers businesses to take control of their software, optimize their processes, and gain a competitive edge through unique, purpose-built solutions. For organizations struggling to find affordable solutions that meet their specific requirements, custom development provides a powerful alternative that can drastically reduce software costs over time.
7 Strategies to Reduce Software Costs Comparison
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Source Software Adoption | Medium - requires technical skills | Low to Medium - largely internal skills | Cost savings, flexibility, security | Cost reduction, avoiding vendor lock-in | No licensing fees, strong community support |
| Software License Optimization | Medium to High - ongoing management | Medium - SAM tools and staff | Cost control, compliance, negotiation leverage | Managing existing licenses effectively | Reduces wasted licenses, avoids penalties |
| Cloud Migration & SaaS Adoption | Medium - cloud governance needed | Medium - cloud management and monitoring | Reduced hardware costs, scalability | Modernization, remote work, flexible costs | Eliminates upfront hardware, scalable |
| Software Standardization | Medium - change management required | Medium - coordination across teams | Bulk savings, simplified support | Large orgs needing consistent software use | Volume discounts, reduced training costs |
| Software Rationalization | High - detailed analysis and change | High - assessment and change management | Reduced app portfolio, complexity | Eliminating redundant or underused software | Lowers maintenance, simplifies IT landscape |
| Vendor Negotiation & Contract Management | Medium to High - expertise needed | Low to Medium - negotiation and tracking | Price and terms improvements | Large contracts, recurring renewals | Cost savings, better contract terms |
| Custom Software Development | High - complex, long-term project | High - development, maintenance teams | Tailored features, competitive edge | Unique business needs, no suitable off-the-shelf solution | Eliminates license fees, exact fit to needs |
Optimizing Your Software Spend: A Path to Greater Efficiency
Reducing software costs isn't a one-time fix, but an ongoing process of refinement. From embracing open-source alternatives and optimizing existing licenses to strategically migrating to the cloud and streamlining your software portfolio, the strategies discussed in this article provide a comprehensive roadmap to significantly reduce software costs. Key takeaways include the importance of software rationalization to eliminate redundancies, the power of vendor negotiation, and the potential of custom software development for unique needs. Mastering these approaches empowers you to not only trim your tech budget but also improve operational efficiency and free up resources for innovation and growth. Whether you're a tech-savvy individual, a family seeking shared access, a small business owner, a student, or a digital nomad, optimizing your software spend translates to direct savings and a more streamlined digital life.
By implementing these strategies, you gain control over your software expenses and pave the way for long-term financial health and technological agility. Want to further amplify your savings and simplify shared access to premium software? Explore AccountShare to unlock the potential of collaborative purchasing and secure account sharing. Visit AccountShare today to discover how you can maximize your software investments while minimizing costs.
