
7 Software Procurement Best Practices for 2025
Share
In today's tech-driven landscape, software is the engine of business growth. Yet, the process of acquiring it is often a complex maze of hidden costs, misaligned expectations, and significant risk. Inefficient software procurement doesn't just waste money; it stifles innovation and leaves organizations vulnerable. Moving beyond reactive purchasing to a strategic, data-driven approach is no longer optional, it's essential for competitive advantage.
This guide presents a curated collection of battle-tested software procurement best practices designed to transform your acquisition process into a well-oiled machine. We will move beyond generic advice to provide actionable frameworks for every stage of the buying journey. You will learn how to define precise requirements, conduct rigorous vendor due diligence, analyze the true total cost of ownership, and negotiate contracts that protect your interests.
By mastering these principles, you can ensure every software investment delivers maximum value, aligns perfectly with business goals, and strengthens your operational and security posture. This listicle provides the blueprint for turning a potential budget drain into a source of strategic gain, setting your organization up for success in 2025 and beyond. Let's dive into the core practices that separate successful procurement teams from the rest.
1. Strategic Requirements Definition and Business Case Development
The most critical errors in software procurement often occur before you even speak to a vendor. One of the foundational software procurement best practices is establishing a rock-solid foundation through strategic requirements definition and a comprehensive business case. This process moves beyond a simple features wishlist to deeply analyze and document the core business problem you aim to solve.
Jumping into vendor demos without this groundwork leads to purchasing decisions based on impressive features rather than actual business needs. This foundational phase ensures every subsequent step, from vendor selection to negotiation, is anchored to clear, measurable objectives. It involves aligning stakeholders, defining solution criteria, and conducting a rigorous Return on Investment (ROI) analysis to validate the expenditure.
Why It's a Foundational Step
Proper requirements definition prevents "scope creep," ensures user adoption, and aligns the final solution with long-term business goals. Companies that excel in this area often dedicate significant resources upfront. For example, a successful Salesforce implementation at a large corporation like T-Mobile required months of requirements gathering across tens of thousands of employees to ensure the platform met diverse departmental needs. Similarly, large-scale SAP implementations often allocate 20-30% of the total project time just to defining and documenting business requirements.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To execute this effectively, move beyond informal discussions and adopt structured techniques:
- Involve End-Users Early: Host workshops with the people who will use the software daily. Use techniques like user story mapping to capture their needs in a practical, scenario-based format.
- Document Everything: Clearly distinguish between functional requirements (what the software must do, e.g., "generate monthly reports") and non-functional requirements (how it must be, e.g., "load reports in under three seconds," "be accessible on mobile devices").
- Create a Traceability Matrix: For complex procurements, a requirements traceability matrix links each business requirement to specific software features and test cases. This ensures nothing is overlooked during implementation and testing.
- Establish a Change Management Process: Define a formal process for how new requirements are requested, evaluated, and approved once the initial scope is set.
The following infographic illustrates the core workflow for this strategic definition phase, ensuring a logical progression from stakeholder collaboration to data-driven decision-making.
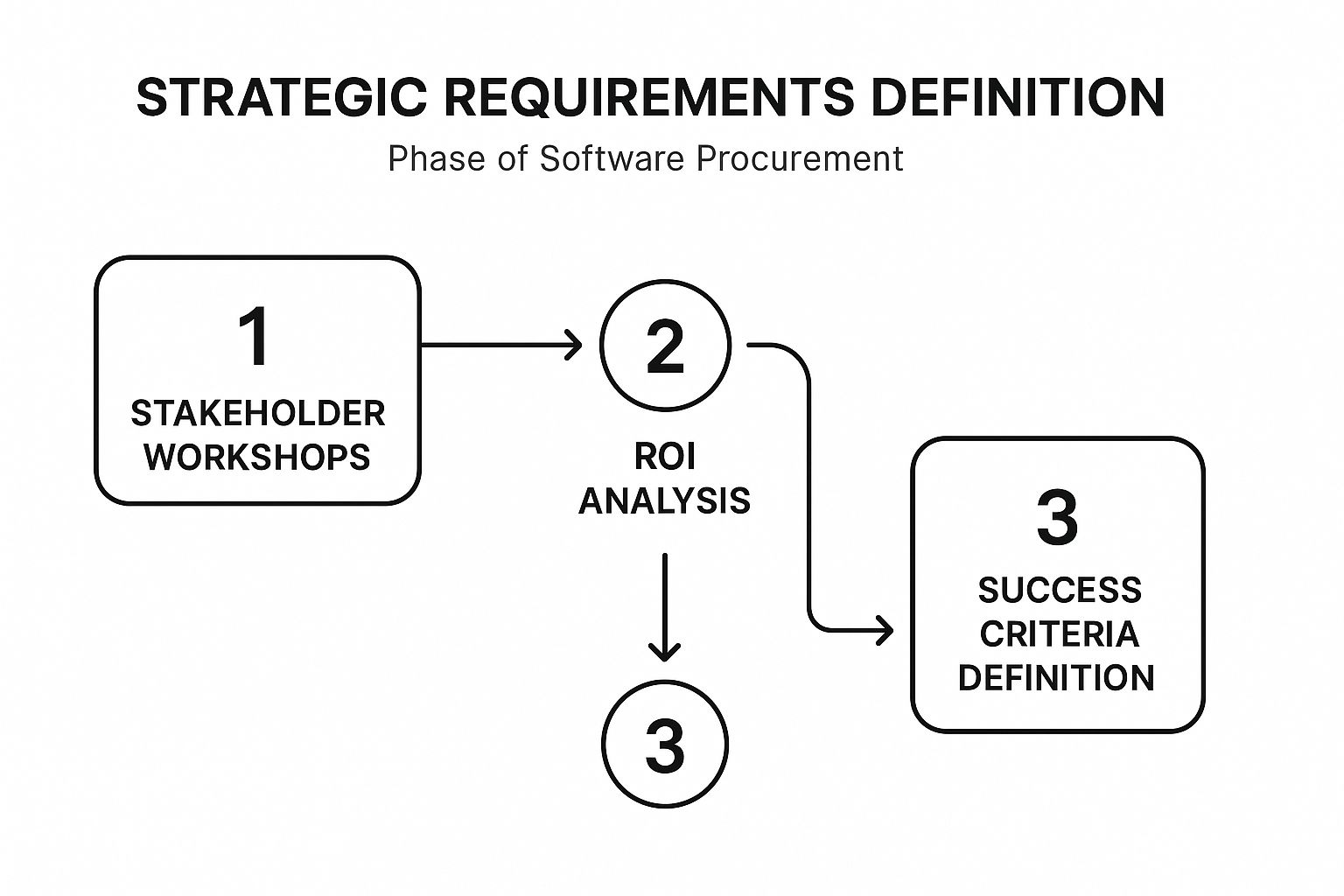
This process flow highlights how each step builds upon the last, culminating in a clear set of success criteria that will guide the entire procurement project.
2. Comprehensive Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis
Focusing solely on the initial licensing or subscription fee is a common but costly mistake. A crucial element of software procurement best practices is conducting a comprehensive Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis. This financial discipline forces you to look beyond the sticker price and evaluate all direct and indirect costs associated with the software over its entire lifecycle, revealing the true financial impact of your decision.

A thorough TCO model includes expenses for implementation, data migration, customization, employee training, ongoing maintenance, support contracts, hardware upgrades, and even eventual decommissioning. Neglecting these hidden costs often leads to significant budget overruns and turns a seemingly affordable solution into a long-term financial drain.
Why It's a Foundational Step
TCO analysis provides a realistic financial forecast, enabling accurate budgeting and preventing unexpected expenses down the line. It offers an "apples-to-apples" comparison between vendors that might have vastly different pricing models. For instance, Gartner's research has shown that a 'cheaper' on-premise CRM could cost 40% more over five years than a SaaS alternative once all maintenance and upgrade costs are factored in. Similarly, TCO studies for complex systems like Oracle databases often reveal that the initial license fee represents only 20-30% of the total cost.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To build a robust TCO model, you must account for every potential cost center:
- Include All Stakeholder Time Costs: Quantify the hours your IT, legal, and business teams will spend on implementation, training, and ongoing management. These internal resource costs are a significant, often-overlooked expense.
- Factor in Inflation and Refresh Cycles: Project costs over a 3-5 year period, accounting for inflation and the potential need for hardware or infrastructure upgrades to support the new software.
- Create Multiple Scenarios: Develop conservative, realistic, and optimistic cost scenarios. This helps you understand the potential range of financial impact and prepare for the worst-case scenario.
- Validate with Vendor References: During due diligence, ask a vendor’s current customers about their actual implementation and maintenance costs to validate the estimates provided by the vendor. For additional insights on financial planning, you can learn more about ways to reduce software costs on AccountShare.ai.
3. Rigorous Vendor Due Diligence and Risk Assessment
Choosing a software vendor is like entering a long-term business partnership. A great product is only one part of the equation; the stability, security, and reliability of the vendor behind it are equally critical. This is where software procurement best practices demand a rigorous due diligence and risk assessment process that goes far beyond a feature-for-feature comparison.
Failing to properly vet a vendor can expose your organization to significant risks, including data breaches from poor security practices, operational disruptions if the vendor fails financially, or project derailment due to inadequate support. A thorough evaluation of a vendor's financial health, security posture, compliance certifications, and support infrastructure is non-negotiable for mitigating these long-term liabilities.
Why It's a Foundational Step
Thorough due diligence protects your investment and your organization's reputation. The massive Equifax breach, for instance, prompted a seismic shift in how enterprises scrutinize their vendors' security protocols. Similarly, the economic uncertainty following major global events forced many companies to re-evaluate the financial stability of their smaller, more vulnerable SaaS providers. Effective due diligence ensures your chosen partner can weather storms and securely handle your data.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To implement a robust vendor assessment, formalize your evaluation process beyond simple conversations:
- Standardize Your Evaluation: Develop a vendor assessment scorecard that rates potential partners on weighted criteria like financial stability, security certifications (e.g., SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001), support responsiveness, and product roadmap alignment.
- Mandate Security Questionnaires: Require vendors to complete standardized security assessment questionnaires, such as the SIG (Standardized Information Gathering) Lite or CAIQ (Consensus Assessments Initiative Questionnaire). This provides a structured overview of their security controls.
- Verify, Don't Just Trust: Independently verify claimed certifications with the issuing bodies. Check customer references, especially for companies of a similar size and industry to your own, to gauge real-world performance and support quality.
- Establish Ongoing Monitoring: Due diligence isn't a one-time event. Implement a process for continuous vendor performance monitoring, including periodic security reviews and risk assessments, to ensure they remain compliant and reliable throughout the contract lifecycle. This is crucial for managing the security of shared or group access credentials. For more on this, you can learn more about managing group access securely at AccountShare.ai.
4. Structured Proof of Concept (PoC) and Pilot Testing
After shortlisting vendors based on proposals and demos, the next critical step is to validate their claims in your unique operational environment. This is where structured Proof of Concept (PoC) and pilot testing become indispensable software procurement best practices. This stage involves a controlled, small-scale deployment of a solution to test its functionality, performance, integration capabilities, and user acceptance before making a significant financial commitment.
A well-executed PoC moves beyond the vendor's perfectly curated demo environment and into the complexities of your actual business workflows. It provides tangible, evidence-based insights into how the software will perform, mitigating the risk of purchasing an expensive solution that ultimately fails to meet expectations. This hands-on evaluation ensures the chosen tool not only has the right features but also fits the company culture and technical infrastructure.

Why It's a Foundational Step
A PoC or pilot is your best defense against post-implementation surprises. It uncovers hidden issues, from usability problems to technical integration challenges, that are impossible to spot in a sales presentation. For instance, major financial institutions often run mandatory 90-day pilots for new trading platforms with a limited group of traders. This allows them to assess performance under real market conditions and gather user feedback before a full-scale rollout. Similarly, NASA requires comprehensive PoCs for mission-critical software, which include simulated failure scenarios to ensure absolute reliability.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To maximize the value of this phase, a structured approach is essential. Avoid informal "tire-kicking" and instead, implement a formal testing plan:
- Define Clear Success Criteria: Before starting, document the specific, measurable outcomes that will define a successful PoC. This could include achieving a certain transaction speed, successfully integrating with a key API, or receiving a minimum user satisfaction score.
- Involve a Representative User Group: Select a diverse group of end-users for the pilot, including power users, casual users, and even skeptics. Their varied perspectives will provide a more holistic view of the software's usability and fit.
- Test Critical Integration Points: Focus the PoC on high-risk areas, especially integration with your existing systems (e.g., ERP, CRM, or proprietary databases). A failed integration is a common reason for project failure.
- Document and Track Everything: Maintain a detailed log of all issues, user feedback, questions, and vendor responses throughout the PoC. This documentation becomes a valuable asset during final evaluations and contract negotiations.
- Set Firm Timelines and Scope: Clearly define the duration (e.g., 30-60 days) and scope of the PoC to prevent it from dragging on indefinitely. A defined endpoint ensures the process remains focused on decision-making.
5. Cross-Functional Procurement Team Formation
Procuring software in a silo is a recipe for failure. An often-overlooked yet vital component of software procurement best practices is the formation of a cross-functional team. This approach intentionally brings together key stakeholders from IT, procurement, legal, security, finance, and the specific business units that will use the software, ensuring a 360-degree evaluation.
When only one department, like IT, drives the procurement process, critical non-technical aspects such as financial implications, legal risks, or practical end-user workflows can be missed. A diverse team prevents these blind spots, leading to a more robust decision that aligns with the entire organization's strategic goals and operational realities. This collaborative foundation dramatically increases the likelihood of successful implementation and widespread user adoption.
Why It's a Foundational Step
A cross-functional team ensures all requirements are captured comprehensively, from technical specifications to compliance mandates. For instance, when healthcare organizations select an Electronic Health Record (EHR) system like Epic, their committees must include clinicians, IT staff, finance experts, and compliance officers. Each group brings a non-negotiable perspective that is essential for a successful outcome. Similarly, Google’s software procurement process famously includes representatives from engineering, legal, security, and business operations to ensure any new tool is secure, scalable, and delivers clear business value.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To build and manage an effective cross-functional team, you need a clear operational framework:
- Define Roles and Authority: Clearly document each member's responsibilities and decision-making power. For example, Legal has final say on contract terms, while the business unit leader has veto power on usability.
- Establish Communication Protocols: Set a regular meeting cadence and use collaborative tools to centralize all documentation, evaluation scorecards, and discussions. To see what might work for your team, you can learn more about team collaboration tools on accountshare.ai.
- Create Escalation Paths: Inevitably, disagreements will arise. Pre-define a clear process for how conflicts are escalated and resolved to prevent project stalls.
- Rotate Leadership by Phase: Consider rotating the team lead based on the procurement phase. A business lead might be best for requirements gathering, while a procurement lead takes over during negotiations.
6. Strategic Contract Negotiation and SLA Definition
Once you have selected a vendor, the procurement process shifts to one of its most high-stakes phases: contract negotiation. This is where you transform business requirements and vendor promises into legally binding commitments. A key aspect of software procurement best practices is moving beyond standard terms to strategically negotiate a contract and Service Level Agreement (SLA) that fully protects your organization and ensures performance.
A poorly negotiated contract can expose your business to significant risks, from unexpected cost overruns and poor vendor performance to data lock-in. The goal is to create a partnership agreement that clearly defines responsibilities, performance metrics, and remedies for failure. This stage is your primary opportunity to secure favorable terms on licensing, support, security, and future scalability.
Why It's a Foundational Step
Strategic negotiation ensures the software delivers on its promised value over the long term. It establishes clear accountability and provides recourse if the vendor fails to meet expectations. For instance, Amazon Web Services (AWS) enterprise contracts are renowned for their detailed SLAs that offer specific service credits for downtime, providing a tangible financial incentive for uptime. Similarly, large Microsoft Enterprise Agreements often include licensing optimization clauses that allow companies to adjust their license counts based on actual usage, preventing overspending.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To negotiate a contract that serves your business interests, adopt a proactive and detail-oriented approach:
- Benchmark Key Terms: Before entering negotiations, research industry-standard terms for similar software. Use this data to benchmark pricing, support levels, and liability clauses to ensure you are getting a fair deal.
- Include Exit Strategy Clauses: Always plan for the end of the relationship. Insist on clear termination assistance and data portability clauses that define how the vendor will help you migrate your data to another system if you choose to leave.
- Negotiate Flexible Licensing: For scalable solutions, push for usage-based or consumption-based pricing models instead of fixed per-user licenses. This allows costs to align directly with actual consumption and business value.
- Define Clear SLA Metrics and Remedies: Don't accept vague promises like "high uptime." Specify exact metrics (e.g., 99.95% uptime measured monthly) and define the penalties for breaches, such as service credits or the right to terminate for repeated failures. Establish a clear escalation path for support issues.
7. Comprehensive Implementation Planning and Change Management
Purchasing the right software is only half the battle; ensuring it is successfully adopted and delivers value is the other half. A core tenet of software procurement best practices is dedicating significant effort to comprehensive implementation planning and change management. This moves beyond a simple technical rollout schedule to address the human and operational side of a new technology investment.
Failing to plan for user adoption and organizational disruption is a primary reason why software investments fail to deliver their expected ROI. This strategic phase ensures that technical deployment, user training, system integrations, and business continuity are managed proactively. It involves creating a detailed roadmap that anticipates resistance, prepares users for new workflows, and aligns the entire organization around the change.
Why It's a Foundational Step
A detailed implementation and change management plan minimizes business disruption, accelerates user adoption, and maximizes the value realized from the new software. Organizations that master this often see much higher engagement and satisfaction rates. For instance, Slack's enterprise implementations succeed because they include comprehensive change management programs with executive sponsors and department champions. Similarly, complex Office 365 migrations often use Microsoft's FastTrack methodology, a structured framework designed to ensure a smooth, well-communicated rollout.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
To build a robust plan, you must integrate technical and human-centric strategies:
- Identify and Train Champions: Select enthusiastic power users early in the process. Train them to become internal champions who can provide peer support, advocate for the new tool, and offer practical guidance to their colleagues.
- Diversify Training Methods: Plan for multiple training delivery methods to accommodate different learning styles. Offer a mix of live workshops, on-demand video tutorials, written documentation, and one-on-one coaching sessions.
- Establish Feedback Loops: Create clear channels for users to provide feedback, report issues, and ask questions during and after the rollout. A rapid-response process to address this feedback is crucial for building user trust and momentum.
- Create Detailed Rollback Procedures: For each phase of the implementation, document a clear rollback plan. This contingency planning provides a safety net in case of critical system failures, ensuring business operations can be quickly restored.
- Communicate Relentlessly: Develop a communication plan that keeps all stakeholders informed about progress, timelines, benefits, and what to expect. Regular updates prevent surprises and manage expectations effectively.
Best Practices Comparison for Software Procurement
| Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Requirements Definition and Business Case Development | High - multi-stakeholder coordination, thorough analysis | Moderate - workshops, documentation, stakeholder time | Clear alignment on needs, reduced scope creep, solid business case | Complex procurements needing precise alignment and ROI clarity | Reduces project failures, enables accurate budgeting, clear vendor evaluation |
| Comprehensive Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis | Medium - extensive data gathering and modeling | Moderate to High - cross-functional input, financial expertise | Accurate long-term budgeting, uncover hidden costs | Financial planning and procurement where full lifecycle costs matter | Prevents budget surprises, supports negotiation, enables fair solution comparisons |
| Rigorous Vendor Due Diligence and Risk Assessment | High - specialized expertise, in-depth evaluation | High - requires security, financial, and compliance checks | Reduced vendor risks, ensured compliance, better contract leverage | Strategic vendor selections with high risk or compliance needs | Mitigates failures and breaches, improves contract terms, early issue detection |
| Structured Proof of Concept (PoC) and Pilot Testing | Medium to High - controlled environment setup and testing | High - dedicated resources, infrastructure, user involvement | Validated solution fit, identified technical and user issues early | Large or critical deployments requiring hands-on validation | Reduces investment risk, strengthens vendor position, user acceptance verified |
| Cross-Functional Procurement Team Formation | Medium - coordination of diverse stakeholders | Moderate - time and facilitation effort | Improved decision quality, reduced silos, better adoption | Procurement projects needing broad input and shared accountability | Comprehensive requirement coverage, accelerated decisions, better buy-in |
| Strategic Contract Negotiation and SLA Definition | High - complex negotiations and legal review | Moderate to High - legal expertise, negotiation effort | Legal protection, predictable costs, clear performance expectations | High value contracts requiring risk mitigation and service guarantees | Protects interests, facilitates vendor transitions, clear accountability |
| Comprehensive Implementation Planning and Change Management | High - detailed planning, cross-team coordination | High - extensive planning, training, communication | Smooth rollout, reduced disruption, improved adoption | Deployments with high user impact and technical complexity | Minimizes risks, improves satisfaction, ensures project tracking and success |
Elevating Procurement from a Task to a Strategic Advantage
Navigating the complex landscape of software acquisition requires more than a simple checklist. It demands a strategic mindset, a commitment to due diligence, and a collaborative spirit. The seven software procurement best practices detailed in this guide, from crafting a precise business case to negotiating ironclad Service Level Agreements, represent a comprehensive framework for transforming procurement from a reactive, administrative task into a powerful engine for strategic growth.
By embracing these principles, you shift the focus from merely acquiring tools to investing in solutions that deliver measurable, long-term value. This journey is about asking the right questions at every stage. Are your requirements truly aligned with business outcomes? Have you uncovered all potential hidden costs in your Total Cost of Ownership analysis? Is your cross-functional team providing a 360-degree view of the potential impact on your organization? Answering these questions with data-backed confidence is the hallmark of a mature procurement strategy.
From Process to Competitive Edge
Mastering these practices yields benefits that extend far beyond cost savings. A well-executed procurement process mitigates significant risks, from cybersecurity threats to compliance violations. It ensures that new software integrates smoothly into your existing tech stack, fostering high user adoption and minimizing disruption. Ultimately, it aligns every software investment directly with your overarching business objectives, ensuring that technology acts as an accelerator, not an anchor.
The key takeaway is that strategic procurement is not a one-time event but an ongoing discipline. It involves:
- Proactive Planning: Moving beyond urgent needs to anticipate future requirements.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Replacing assumptions with rigorous analysis, from vendor financials to performance metrics in a Proof of Concept.
- Holistic Value Assessment: Looking past the sticker price to understand the true impact on efficiency, security, and innovation.
This disciplined approach ensures that your software portfolio is not just a collection of licenses but a curated ecosystem of tools that empowers your teams, delights your customers, and drives your organization forward. The commitment to these software procurement best practices is a direct investment in your company's operational excellence and competitive resilience.
The Future is Collaborative and Cost-Effective
As you refine your internal processes, remember that the software market itself is evolving. Innovative models like group purchasing and account sharing are creating new avenues for cost optimization without sacrificing access to premium tools. By integrating these modern strategies with the foundational best practices we've discussed, you position your organization at the forefront of intelligent, efficient, and forward-thinking software management.
Ready to put these principles into action and unlock significant savings on your essential software tools? Discover how AccountShare can help your team leverage collective buying power, reducing costs on premium subscriptions while maintaining secure and organized access. Visit AccountShare to learn how you can make your software budget go further.
