
User Roles and Permissions: Complete Security & Access Guide
Share
Understanding User Roles and Permissions Fundamentals

User roles and permissions form the foundation of a secure system. They control access, protecting data and ensuring smooth operations. This section explores the key concepts of access control and explains their importance.
Authentication Vs. Authorization: Two Sides Of The Same Coin
First, it's important to understand the difference between authentication and authorization. Authentication confirms a user's identity, much like verifying a username and password. Authorization, on the other hand, dictates what a user can do after their identity is verified.
Think of it this way: logging into your email is authentication. Being able to access only your inbox, not someone else's, is authorization.
The Principle Of Least Privilege: A Cornerstone Of Security
Effective user roles and permissions systems adhere to the principle of least privilege. This means granting users only the minimum access required to perform their duties. This strategy minimizes potential damage from security breaches or accidental mistakes.
Imagine a scenario where every employee has administrator access. A single wrong click could have catastrophic consequences.
The Rise Of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a widely used method for managing user access. Instead of assigning individual permissions, RBAC groups permissions into roles. Users are then assigned to these roles based on their job responsibilities.
This streamlines administration and creates consistency in access control, especially important with the growing use of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies. As more employees access company resources on personal devices, RBAC helps organizations maintain security across various devices. Learn more about RBAC and BYOD trends here.
Key Benefits Of Well-Defined User Roles And Permissions
A robust system for user roles and permissions provides several important advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Limiting access reduces the risk of unauthorized data access and changes.
- Improved Compliance: Many regulations mandate strict access controls. A well-designed system helps meet these requirements.
- Streamlined Administration: RBAC simplifies user access management, particularly in large organizations.
- Increased Productivity: Users can quickly access necessary resources, leading to better workflow.
- Reduced Errors: Clearly defined permissions minimize accidental data deletion or modification.
For further insights, check out this resource: How user permissions management can boost security and efficiency. It emphasizes the importance of access control and provides guidance on building a secure system. Managing user access is an ongoing process that demands planning and careful execution, but the rewards are significant.
Choosing The Right Access Control Model For Your Needs
Selecting the right access control model is crucial for balancing security and usability. This involves understanding different models and their alignment with your specific organizational needs. Let's explore some key considerations for making the informed choice.
Understanding Different Access Control Models
Several access control models exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these distinctions is fundamental to choosing the best solution for your organization.
-
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC simplifies user management by assigning permissions to roles rather than individual users. This method is highly effective for larger organizations where managing individual permissions can become incredibly complex.
-
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): ABAC offers more granular control by considering attributes of users, resources, and the environment. This model facilitates dynamic and context-aware access decisions but can be more challenging to implement.
-
Hybrid Approaches: Combining elements of RBAC and ABAC can offer a flexible and scalable solution. This allows organizations to benefit from the standardized structure of roles while also maintaining granular control when necessary.
Evaluating Your Needs and Resources
Choosing the optimal access control model involves a thorough assessment of your specific organizational context.
-
Organizational Size and Structure: A large organization with a complex hierarchy may benefit from the streamlined approach of RBAC. A smaller, more agile organization might find the flexibility of ABAC a better fit.
-
Security Requirements: Highly sensitive data may necessitate the fine-grained control provided by ABAC. Less sensitive data may be adequately protected with RBAC.
-
Technical Expertise: Implementing and managing ABAC generally requires more specialized knowledge than RBAC. Consider your team's current capabilities and the potential need for additional training or external consultants.
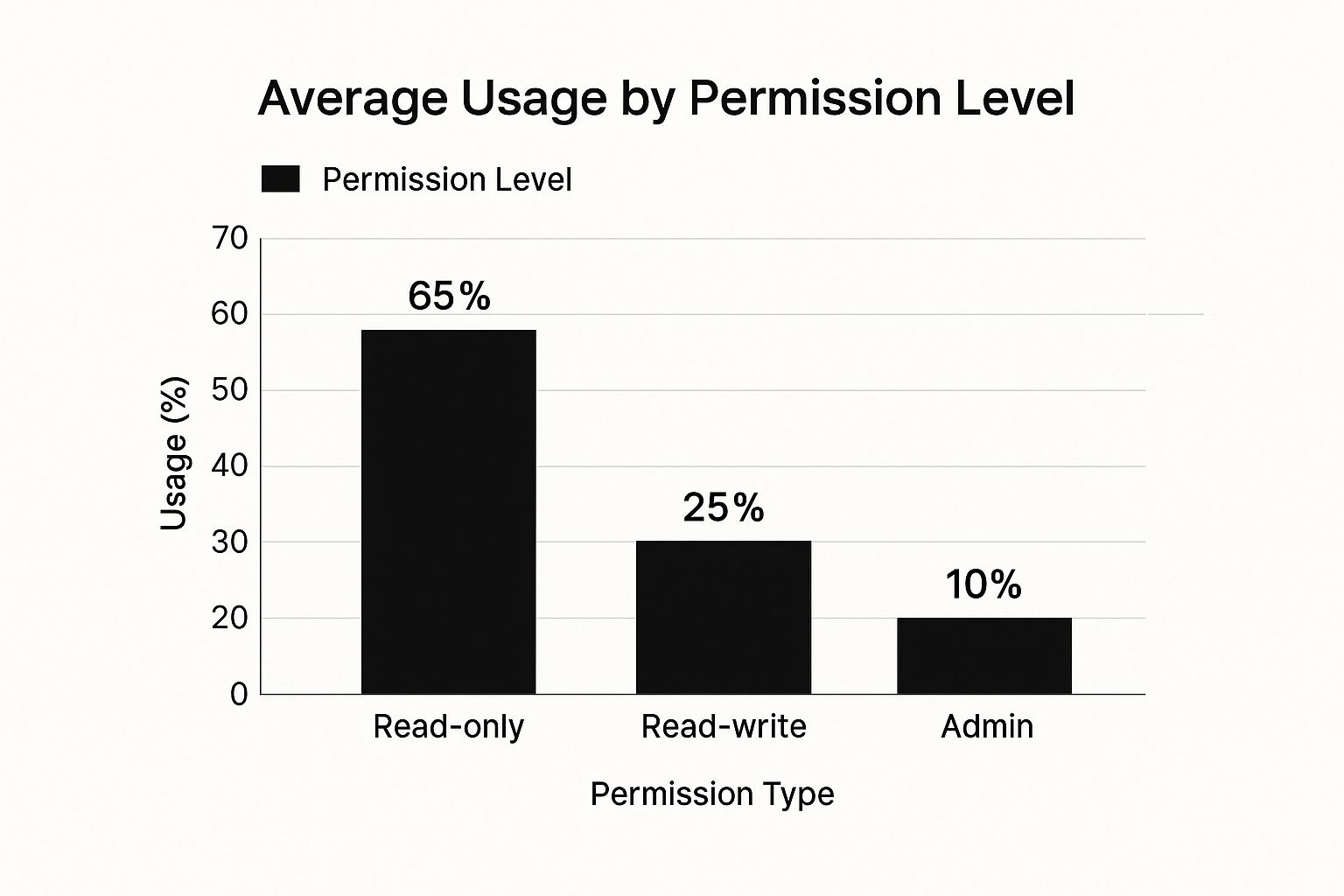
The infographic above visualizes the average usage percentages of different user permission levels: Read-only (65%), Read-write (25%), and Admin (10%). This data highlights that a majority of users require only read-only access. Assigning permissions based on the principle of least privilege is critical. Granting excessive permissions significantly increases security risks and administrative overhead.
To help you compare the different models we've discussed, take a look at the following table:
Access Control Model Comparison: This table compares different access control models, highlighting their key features, use cases, security levels, and implementation complexity.
| Model Type | Security Level | Complexity | Best Use Cases | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBAC | Moderate | Low | Large organizations with clearly defined roles | High |
| ABAC | High | High | Environments requiring granular, context-aware access control | Moderate |
| Hybrid | Moderate to High | Moderate to High | Organizations needing both role-based and attribute-based control | Moderate to High |
This comparison underscores the importance of choosing a model that aligns with your organization’s specific needs and resources. RBAC excels in scalability and ease of implementation, while ABAC offers greater flexibility and security. Hybrid models aim to bridge the gap, combining the strengths of both.
Balancing Security and Usability
A key challenge in access control is finding the right balance between robust security and user-friendliness. Overly restrictive access controls can hinder productivity, while excessive access creates vulnerabilities. RBAC often strikes a good balance for many organizations, but ABAC or hybrid models might offer more fine-tuned control when required. Read also: How to master effective group access control to secure and streamline your systems.
Making the Decision
Several factors should guide your decision when selecting an access control model:
-
Scalability: Choose a model that can adapt as your organization expands.
-
Maintenance: Consider the ongoing maintenance requirements and ensure they align with your available resources.
-
Integration: Verify compatibility with your current systems and infrastructure.
-
Cost: Evaluate the overall cost, including implementation, maintenance, and potential training expenses.
Making a well-informed decision about access control will benefit your organization in the long term by bolstering security, streamlining administration, and improving the user experience. The right access control model empowers your users while minimizing risk, strengthening your overall security posture, and enabling more efficient operations.
Building Role Hierarchies That Scale With Your Business

Creating a sustainable structure for user roles and permissions requires a deep understanding of your current needs and, importantly, your future growth. This means anticipating how access control will need to adapt as your business expands and evolves.
Designing For Growth: Avoiding Role Explosion
A common pitfall is role explosion, where the sheer number of roles becomes overwhelming. Imagine a company creating a new role for every slight variation in a job. This quickly creates an administrative nightmare and opens the door to security risks.
Instead, start with broader roles encompassing a wider range of responsibilities. This simplifies management and onboarding. As you grow, refine these roles, but a manageable foundation is key.
Mapping Job Functions To Access Levels
Mapping job functions to the right user roles and permissions is critical for effective access control. Begin by identifying the core duties of each job title. Then, determine the minimum access required, following the principle of least privilege.
For example, a marketing team member might need access to social media platforms like Facebook and email marketing software like Mailchimp, but not to sensitive financial data. Defining these needs prevents permission creep, where users accumulate excessive access over time.
Governance Frameworks: Keeping Your System Healthy
A strong governance framework ensures your system remains robust. This includes:
-
Regular Audits: Periodic reviews of user access to identify discrepancies or unnecessary permissions.
-
Automated Monitoring: Systems that automatically flag suspicious activity or potential security breaches.
-
Clear Documentation: Maintain updated records of roles, permissions, and governance procedures.
These practices help prevent security issues and ensure compliance. For further information, see this helpful article: Top access control best practices for 2025.
Handling Edge Cases: Contractors And Temporary Staff
Think about access for non-employees, like contractors or temporary staff. These individuals often need specific, time-limited access. Dedicated roles or temporary credentials can address this without compromising security.
Future-Proofing Your Role Structure
Forward-thinking businesses anticipate future needs and build flexibility into their system. Consider these strategies:
-
Modular Roles: Designing roles in a modular fashion allows for easy adaptation as new technologies or processes emerge.
-
Dynamic Permissions: Systems that automatically adjust permissions based on context, like location or time.
By planning ahead, you can create a system that effectively supports your business's growth and evolution.
Implementation Strategies That Deliver Results
Moving from planning user roles and permissions to actual implementation requires careful consideration of both technical hurdles and the impact on your team. This section provides a practical roadmap, drawing on successful implementations across various organizations. We'll explore how IT leaders can gain buy-in, manage resistance, and even integrate older systems, ultimately delivering measurable security enhancements.
Phased Implementations: Minimizing Disruption, Maximizing Impact
Implementing new user roles and permissions doesn't have to be a disruptive, overnight change. A phased approach allows for incremental adjustments, minimizing disruptions to daily operations while still providing tangible security benefits.
For example, consider starting with a pilot program within a specific department or focused on one particular system. This allows for thorough testing and refinement before a broader rollout. Furthermore, early successes in the pilot program can generate positive momentum and demonstrate the value of the changes to key stakeholders. This controlled, measured approach reduces risk and provides invaluable learning opportunities.
Securing Stakeholder Buy-In: A Critical Success Factor
Gaining support from key stakeholders is crucial for a smooth implementation. Clearly communicate the advantages of the new system, highlighting improved security, more efficient administration, and a reduced risk of security breaches. Proactively address any concerns and involve stakeholders in the planning stages.
For instance, showing how the new system aligns with regulatory requirements like SOC 2 can be especially convincing. This ensures everyone understands the rationale behind the change and fosters a sense of shared ownership.
Managing User Resistance: Addressing the Human Element
Change can be difficult. Users may resist adopting new systems, especially if they perceive them as complicated or disruptive to their established workflows. Provide sufficient training and support to ease the transition. Clearly explain the benefits of the new system and address user concerns directly.
Open communication and continuous support are essential for successful adoption. A well-informed user base is much more likely to embrace the new system and realize its advantages.
Legacy System Integration: Bridging the Old and the New
Integrating user roles and permissions with legacy systems can present a significant challenge. A thorough assessment of existing systems and data flow is essential for successful integration. Prioritize integrations based on business needs and allocate resources accordingly.
One effective strategy involves using APIs and integration platforms like Mulesoft Anypoint Platform to connect the new system with legacy applications. This reduces manual data entry and ensures data consistency across all systems. However, it’s important to be prepared for unexpected complications and build flexibility into your implementation plan.
Establishing Realistic Timelines and Resource Allocation
Accurate timelines and sufficient resources are fundamental to implementation success. Underestimating the required time and effort can lead to delays and frustration. Involve experienced IT professionals in the planning phase to develop realistic estimations.
Secure an adequate budget and appropriate staffing to support the project throughout its entire lifecycle. This includes resources for training, testing, and ongoing maintenance. Proper resource allocation ensures a smoother implementation and promotes long-term system health.
Testing Protocols: Catching Issues Before They Impact Users
Thorough testing is vital to identify and resolve problems before they affect users. Develop comprehensive testing protocols that cover all aspects of the system, including user authentication, authorization, and data integrity.
For instance, simulate real-world scenarios to test system performance under different conditions. This helps you identify and address potential vulnerabilities proactively. Regularly review and update your testing procedures to maintain their effectiveness and relevance.
Learning from Setbacks: The Path to Resilience
Not every implementation will be flawless. Be prepared for unforeseen challenges and develop a plan to address setbacks. Open communication and collaboration among team members are critical for navigating difficulties and finding solutions. Document lessons learned to prevent repeating mistakes. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and builds organizational resilience.
Market Dynamics And Strategic Investment Considerations

Understanding current trends in access control helps organizations make informed decisions about technology investments and avoid costly mistakes. This involves analyzing market forces that drive the need for robust user roles and permissions systems.
The Rise of RBAC and Its Market Impact
One key trend is the growing adoption of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). RBAC simplifies user access management by assigning permissions to roles instead of individual users. This is especially helpful for large organizations with complex structures.
The rise of remote work and cloud migration has further emphasized the importance of robust access control. These shifts require secure and flexible systems for managing user access across various locations and devices.
This increasing demand has fueled significant growth in the RBAC market. In 2022, the market was valued at approximately USD 8.5 to 8.7 billion across various reports. Forecasts predict continued expansion, with CAGR ranging between 10% and 14.5% from 2023 to around 2030-2032. You can find more detailed statistics here: RBAC Market Research.
To further illustrate the projected growth, let's look at the following table:
RBAC Market Growth Projections
| Research Source | 2022 Value (USD Billion) | Projected Value (USD Billion) | Target Year | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MarketsandMarkets | 8.5 | 20.1 | 2027 | 18.8 |
| Grand View Research | 8.7 | 22.7 | 2030 | 10.6 |
| Fortune Business Insights | 8.6 | 19.7 | 2029 | 13.1 |
This table summarizes key market projections from different research sources, highlighting the expected growth in the RBAC market. The variation in projected values and CAGRs reflects different methodologies and assumptions used by each research firm.
Regulatory Compliance and Cybersecurity Threats
Regulatory compliance is another major driver of investment in access control. Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX mandate strict controls over data access and security. Organizations must implement strong user roles and permissions systems to meet these requirements and avoid penalties.
The constantly changing cybersecurity landscape also presents significant threats. Data breaches and cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated, making strong access controls vital for protecting sensitive information.
The Cost of Inadequate Access Management
Failing to invest in adequate access management can have significant financial and reputational consequences. Data breaches can lead to substantial fines, legal fees, and damage to brand reputation.
Inefficient access control processes can also lead to lost productivity and increased operational costs. For example, if employees lack access to needed resources, they may be unable to complete tasks efficiently, resulting in project delays.
Emerging Technologies and the Future of Access Control
Emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are changing the access control landscape. These technologies allow for smarter and more adaptive access decisions based on user behavior, context, and risk factors.
This means access control systems can become more proactive in identifying and mitigating potential security threats, improving overall security posture. AI-powered systems can analyze user activity patterns to detect unusual or potentially harmful behavior.
Building a Business Case for Modernization
Justifying investment in modernized access control requires a clear business case that resonates with executives. This involves demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) through metrics like a reduced risk of data breaches, improved compliance, and increased operational efficiency.
Metrics for Measuring Success
Organizations use various metrics to measure the success of their access control investments. These include:
-
Reduction in security incidents: Tracking the number of data breaches and unauthorized access attempts.
-
Improved compliance rates: Monitoring compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
-
Streamlined user provisioning: Measuring the time required to grant and revoke user access.
-
Enhanced user experience: Gathering user feedback on the usability of the system.
By tracking these metrics, organizations can demonstrate the value of their access control investments and find areas for improvement. This data-driven approach ensures access control systems remain effective and contribute to the organization’s security and operational goals.
Maintaining Excellence Through Monitoring And Optimization
Maintaining a robust system of user roles and permissions isn't a set-it-and-forget-it task. It requires ongoing attention, regular checks, and continuous improvement. This ensures your access control system remains effective, adapts to changes, and consistently strengthens your security.
Proactive Monitoring: Catching Anomalies Before They Escalate
High-performing organizations use proactive monitoring to identify unusual activity before it becomes a security incident. This involves implementing automated systems, such as those offered by Splunk, that track user access patterns and flag anything out of the ordinary.
For example, if a user suddenly accesses files or systems they don't normally use, the system can trigger an alert. This allows security teams to investigate and prevent potential damage. This proactive approach maintains security while minimizing disruptions.
Regular Audits: Ensuring Continued Best Practices
Regular audits are vital for a healthy access control system. Audits involve reviewing user access rights to ensure they're appropriate and aligned with the principle of least privilege. This principle dictates that users should only have the minimum access necessary to perform their job duties. Audits help identify and correct instances of excessive or unnecessary access.
This might involve checking if former employees still have active accounts, or if current employees have accumulated permissions they no longer need. Consistent audits are essential for maintaining security and compliance.
Streamlining Access Reviews: Efficiency and Security
Access reviews don't have to be a burden. Practical approaches, like automated reporting and targeted reviews of high-risk roles, provide effective oversight without overwhelming your staff. This focuses efforts where they're most needed.
For instance, prioritize reviews of administrator accounts or roles with access to sensitive data. This targeted approach allows for efficient use of resources while maintaining a strong security posture.
Governance Frameworks: Adapting To Evolving Needs
A well-defined governance framework is essential for a sustainable access control system. This framework should outline clear procedures for granting, modifying, and revoking user access. It also includes guidelines for audits and incident response.
Furthermore, the framework should be adaptable. As your business evolves, so should your governance structure, ensuring it remains relevant and effective. This flexibility allows your access control system to keep pace with growth and change.
Optimization Based on Usage Patterns: Data-Driven Decisions
Forward-thinking organizations optimize their role structures based on real-world usage. By analyzing user interactions with the system, you can identify areas for improvement and refine your access control policies. Tools like Mixpanel can help with this analysis.
This data-driven approach helps eliminate redundant roles, consolidate permissions, and tailor access to actual needs, maximizing both efficiency and security.
Building Sustainable Processes: Long-Term Security Health
Sustainable processes are critical for long-term security. This involves automating tasks like user provisioning and de-provisioning, which reduces manual effort and the risk of human error. Tools like Okta can assist with automating these processes.
Clear documentation of all processes and procedures ensures consistency and facilitates smooth transitions within the IT team. These practices create a robust and resilient access control system that strengthens your security posture over time.
Ready to improve your shared account management? Explore AccountShare for efficient and secure access. Get started with AccountShare now!
