
Transform Your Business with the Collaborative Consumption Business Model
Share
The New Economics of Sharing: Understanding Collaborative Consumption

The collaborative consumption business model, also known as the sharing economy, marks a significant shift from traditional ownership. Rather than focusing on individual purchases, it emphasizes access to goods and services. This change creates new economic opportunities for businesses and consumers alike. Businesses can offer more flexible and affordable options, while consumers can enjoy a wider range of products and services without the commitment of ownership.
The Three Pillars of Collaborative Consumption
This emerging economic model rests on three key systems. First, product service systems optimize the use of existing resources. Consider Zipcar, a car-sharing service where vehicles are continuously utilized, generating income and lessening the need for private car ownership.
Second, redistribution markets, such as eBay or ThredUp, extend the life of products. They allow used goods to find new homes, reducing waste and promoting a more sustainable approach to consumption.
Finally, collaborative lifestyle platforms like Airbnb connect people within communities. These platforms facilitate the sharing of resources like accommodations, skills, and even meals, showcasing the versatility of the sharing economy.
The collaborative consumption business model has seen impressive growth. In 2024, the global sharing economy market was valued at approximately $366.2 billion. This number is expected to reach $1.4 trillion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.8% between 2024 and 2030.
Several factors contribute to this growth, including increased urbanization and shifting consumer preferences. Urban environments often lead to higher demand for shared resources, and changing consumer behavior, especially among younger demographics, favors access over ownership and experiences over possessions. The sharing economy also appeals to a growing environmental awareness, as people seek ways to minimize their environmental impact. For more detailed statistics, see: Sharing Economy Growth.
The Value Proposition: A Win-Win Scenario
These systems present a compelling value proposition for both businesses and consumers. Businesses gain opportunities for improved efficiency, lower overhead costs, and entry into new markets. They can optimize resource allocation, minimize waste, and boost profits. Collaborative platforms also offer insights into consumer trends, enabling businesses to personalize their offerings and improve the customer experience.
Consumers, in turn, enjoy lower costs, added convenience, and access to a broader spectrum of goods and services. They can experience high-quality products and services without the financial commitment of ownership, embracing flexibility and convenience. This adaptable approach is especially appealing in today’s fast-paced world. You might be interested in: Our Blogs.
This innovative model tackles inefficiencies inherent in traditional business models. By optimizing resource use and promoting collaboration, collaborative consumption offers a more sustainable and equitable way forward. It builds a foundation for a more efficient, accessible, and environmentally responsible marketplace, highlighting the transformative potential of this collaborative approach.
Industries Transformed: Where Collaboration Beats Ownership
The collaborative consumption business model is reshaping industries. From transportation and accommodation to workspaces and fashion, access to goods and services is fundamentally changing. This section explores how collaboration is outcompeting traditional ownership.
Redefining Transportation and Accommodation
The transportation sector has been significantly impacted by collaborative consumption. Companies like Uber and Lyft have disrupted taxi services by connecting drivers and riders through digital platforms. This allows for flexibility and efficiency, benefiting both drivers and passengers.
Similarly, Airbnb has revolutionized short-term stays. Connecting travelers with hosts offering their homes creates a wider range of options and more personalized experiences than traditional hotels.
Transforming Workspaces and Fashion
The workspace sector is also shifting. WeWork provides flexible, collaborative workspaces, offering an alternative to traditional office leases. This allows businesses, particularly startups and small businesses, to access professional environments without the commitment of long-term leases.
In fashion, platforms like Rent the Runway challenge traditional retail. Consumers can rent high-end clothing, accessing luxury fashion without the high cost of ownership.
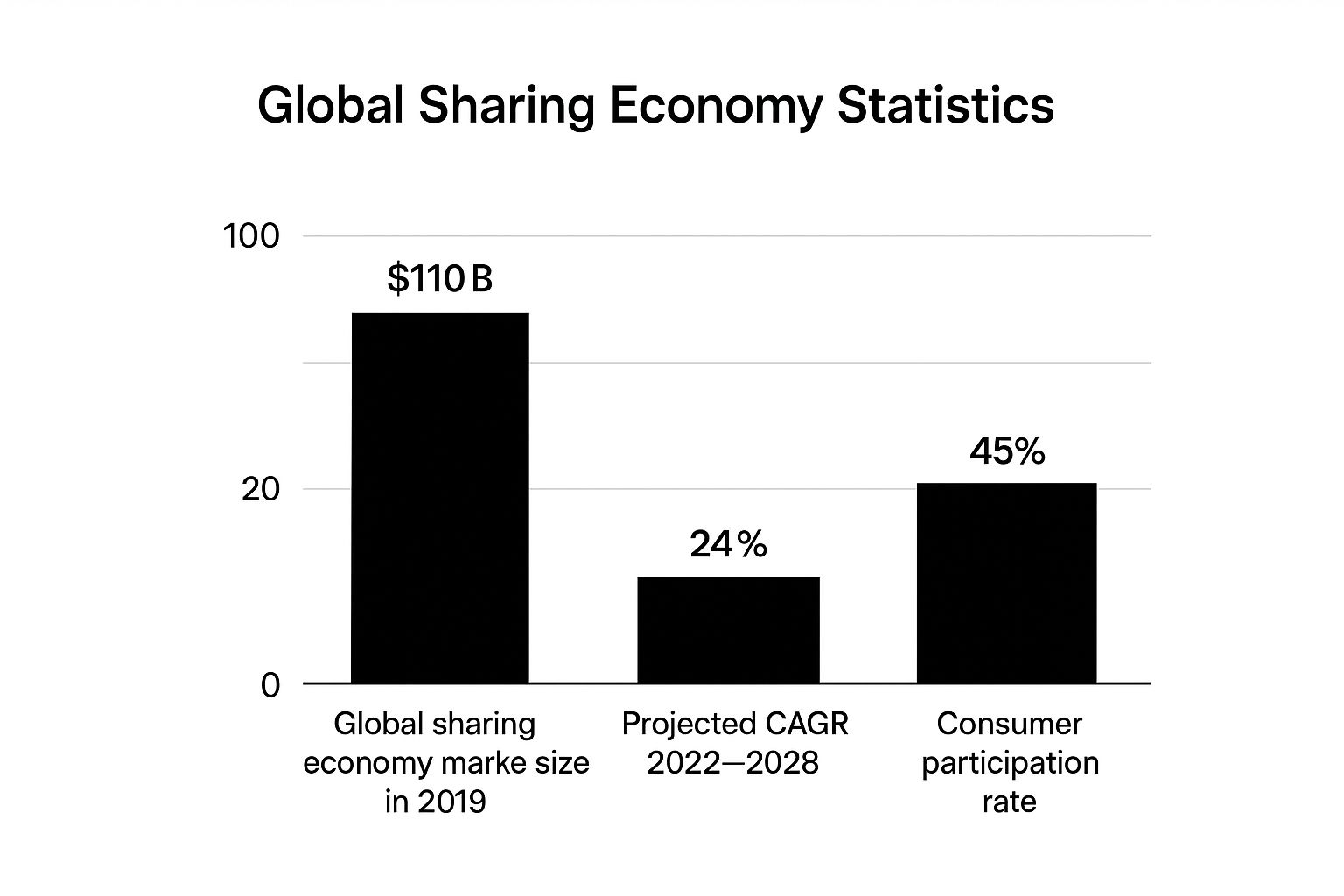
The infographic above visualizes the sharing economy's growth, showing the 2019 market size, projected CAGR, and current consumer participation. These metrics illustrate an expanding market with significant consumer adoption, indicating strong potential for future growth.
To further illustrate the current market landscape, let's take a look at the following table:
Market Leaders Across Collaborative Consumption Sectors
| Sector | Leading Companies | Business Model Type | Revenue Model | Market Valuation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation | Uber, Lyft | Peer-to-peer | Commission based | Uber: $91B (Nov 2023), Lyft: $4.3B (Nov 2023) |
| Accommodation | Airbnb | Peer-to-peer | Commission based | $73.6B (Nov 2023) |
| Workspace | WeWork | Shared Space | Membership/Rental Fees | $2.3B (Nov 2023) |
| Fashion | Rent the Runway | Subscription/Rental | Rental/Subscription Fees | Private |
This table shows the diverse range of successful companies operating within the collaborative consumption framework. It highlights the dominant peer-to-peer and shared space models and how these companies generate revenue. Note the varying market valuations, reflecting the maturity and scale of these businesses.
The Driving Forces Behind Adoption
Several factors contribute to the rise of collaborative consumption:
- Cost Savings: Sharing resources can significantly lower costs.
- Convenience: On-demand access offers increased convenience and flexibility.
- Sustainability: Sharing promotes resource efficiency and reduces waste.
- Technological Advancements: Mobile technology and digital platforms enable seamless operation.
Growing Market Diversity and Projections
This growth isn't limited to a few areas. The sharing economy is diversifying. The market is projected to grow by $1.12 trillion from 2025 to 2029, with a CAGR of 32.3%. Online ride-hailing services are a key contributor to this growth. For more statistics, see: Sharing Economy Market Growth.
The Future of Collaborative Consumption
Collaborative consumption is transforming how we live, work, and consume. As technology evolves and consumer preferences shift, this model is poised for continued growth. Understanding the key drivers of this model is essential for businesses. From equipment rentals to co-working spaces, shared access is creating new markets. Growing environmental awareness further fuels this movement, as consumers seek sustainable alternatives. The potential for further innovation within this framework is immense.
The New Consumer: Demographics Driving Collaborative Markets

The rise of the collaborative consumption business model isn't accidental. It's fueled by distinct demographic trends. Understanding these trends is key for businesses hoping to capitalize on this expanding market. It requires examining how various generations interact with sharing platforms and their motivations.
Millennials and Gen Z: The Sharing Natives
Millennials and Gen Z are now the dominant users of collaborative consumption platforms. This stems from their inherent comfort with technology and their preference for experiences over material goods. They're more likely to use services like Uber and Lyft than own a car, and favor services like Rent the Runway over traditional shopping. This preference for access over ownership is a perfect match for collaborative consumption.
Older Demographics and Niche Markets
While younger generations are the heavy users, older groups are also increasingly adopting these platforms, especially within niche areas. They might embrace home-sharing platforms for extra income or use shared workspaces for the flexibility. This shows that collaborative consumption has a wider appeal than many realize.
Urbanization and Financial Factors
Urban environments are ideal for resource sharing. High population density and limited space make collaborative models extremely attractive. This encourages smart resource use, which sharing platforms facilitate. Also, financial pressures make alternative ownership models more and more appealing. The option to access goods and services without the cost of full ownership broadens the consumer base.
The sharing economy's influence is significant. In 2024, the market size reached $194.14 billion, projected to hit $631.32 billion by 2029. This growth is driven by aging populations, globalization, and even climate change. Learn more about this growth here. For additional information, see this article.
Environmental Awareness and the Impact of the Pandemic
Growing environmental awareness also plays a vital role. Consumers are increasingly conscious of their environmental footprint, and shared consumption offers a greener alternative to traditional ownership. Sharing reduces waste and supports a circular economy. The COVID-19 pandemic also had a substantial impact, boosting some models while hindering others. Remote work fueled the demand for shared workspaces, while travel restrictions impacted short-term rentals.
Understanding the Drivers of Engagement
Understanding the motivations of different demographic groups is essential for platform success. Cost savings are a major draw, but convenience, flexibility, and community are also key. Platforms that effectively address these diverse needs will be best positioned for growth. This knowledge enables businesses to tailor their products and marketing to reach and resonate with their target audience.
Building the Trust Engine: Platform Credibility by Design
Trust is absolutely essential for the collaborative consumption business model. It forms the foundation upon which these platforms operate. Without trust, people would be hesitant to share personal assets like homes, cars, or other possessions with strangers. This section explores the key mechanisms that build and maintain trust in these online marketplaces.
Rating Systems: Shaping User Behavior
Effective rating systems have profoundly impacted consumer behavior in the sharing economy. Platforms like Airbnb and Uber rely heavily on user reviews to cultivate trust. These systems provide transparency, enabling potential users to assess the reliability and quality of services offered by others.
This peer-to-peer feedback creates accountability and fosters positive interactions. For example, an Airbnb host with consistently high ratings is more likely to attract future guests. This highlights the importance of providing exceptional service and cultivating a positive reputation on the platform.
Verification and Insurance: Reducing Uncertainty
Different sharing economy platforms use various verification processes based on their unique requirements. Airbnb might conduct background checks for hosts, while ride-sharing services verify driver's licenses and insurance coverage. These processes add a layer of security, boosting user confidence and mitigating potential risks.
Insurance frameworks also play a vital role in addressing potential problems. By offering coverage for both providers and users, platforms manage potential liabilities and create a safer transaction environment. This comprehensive approach to risk management is a cornerstone of trust-building.
Learning from Trust Failures: Valuable Insights
Even with robust systems in place, trust can sometimes be broken. Analyzing these instances offers important learning opportunities for platform developers. Cases of fraud or security breaches, for example, highlight vulnerabilities and areas where security measures can be strengthened.
Examining high-profile trust failures and how they were addressed provides valuable insights into designing more resilient systems. Addressing these issues openly and proactively, through clear communication and effective solutions, is critical for restoring user trust and preventing future problems. This demonstrates a commitment to platform integrity and user safety.
Balancing Platform Control and Community Ownership
Maintaining trust requires finding a balance between platform control and community self-governance. While platforms establish the rules and guidelines, encouraging a sense of community ownership empowers users. This can be achieved by providing clear channels for feedback and incorporating user suggestions into platform development.
Successful marketplaces demonstrate how engaging the community reinforces trust and promotes responsible user behavior. By allowing users to participate in shaping the platform's evolution, a collaborative environment emerges where trust becomes a shared responsibility.
Building Strong Trust Architectures
A robust trust architecture is vital for the long-term viability of any collaborative consumption platform. This involves implementing multiple layers of security, transparency, and community engagement. From clear communication and user-friendly interfaces to robust dispute resolution mechanisms, every element contributes to building trust.
Platforms prioritizing these elements create a solid foundation for sustainable growth. They attract both users and providers, fostering a thriving and dynamic marketplace. This proactive approach to building trust, addressing potential risks while empowering the community, is essential for success in the collaborative consumption model.
Technology Enablers: The Infrastructure of Sharing

Collaborative consumption businesses depend deeply on technology for smooth operation. From initial connections between users to final payment processing, technology forms the core of these platforms. This exploration delves into the key technological pieces that empower these innovative ecosystems. Robust technological infrastructure, including features like omnichannel customer service, is essential for collaborative consumption platforms to thrive.
Essential Components for Seamless Sharing
A few core technologies are essential to the success of any collaborative consumption platform.
-
Payment Processing: Secure and efficient payment gateways are vital for facilitating transactions. Consider the simplicity of paying for an Airbnb stay or an Uber ride. This smooth, frictionless payment experience is crucial for user satisfaction.
-
Identity Verification: Trust is paramount, and robust identity verification processes are key to building it. Platforms must confirm the authenticity of users, regardless of whether they are renting a car or providing a professional service.
-
Geolocation: Real-time location data is the foundation of many collaborative platforms. Ride-sharing apps, for instance, use geolocation to link drivers with passengers quickly and effectively. This real-time tracking is at the heart of how these services function.
-
Matching Algorithms: Sophisticated algorithms are the engine behind matching users with relevant services and products. Think about how Netflix suggests films based on your viewing history. These algorithms are essential to personalizing the user experience and driving engagement.
The Mobile Revolution and On-Demand Sharing
The widespread adoption of mobile technology created the perfect environment for on-demand services. Smartphones, with their constant connectivity and accessibility, became the driving force behind these sharing platforms. This readily available technology is a significant catalyst in the growth of collaborative consumption.
For example, ride-sharing would not be nearly as convenient without the widespread use of smartphones. The ability to request a ride from anywhere, at any time, has completely changed how we think about transportation in cities. This shift highlights the influence of mobile technology on collaborative consumption. For more information, you might want to check out this resource: Learn more in our article about sitemap.
Emerging Technologies: Transforming the Landscape
New technologies are constantly reshaping the collaborative consumption landscape.
-
Blockchain: This technology provides enhanced security and transparency, particularly for transactions and identity verification. It offers a decentralized and tamper-proof system for managing sensitive data.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI helps optimize marketplace efficiency by personalizing recommendations, forecasting demand, and refining matching algorithms. It allows platforms to learn from user behavior and improve their offerings.
-
Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT unlocks possibilities for sharing entirely new types of assets. Imagine renting out your smart appliances or providing access to your connected car. The potential is vast.
To better illustrate how these technologies are affecting collaborative business models, let's look at the following table:
Technology Impact on Collaborative Business Models
This table shows how different technologies are transforming various aspects of collaborative consumption business models and their implementation across different sectors.
| Technology | Primary Impact | Implementation Examples | Future Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payment Processing | Streamlined transactions, increased security | Mobile payments, in-app purchases | Micropayments, automated payouts |
| Identity Verification | Increased trust and safety | Secure logins, background checks | Decentralized identity systems |
| Geolocation | Real-time tracking and matching | Ride-sharing, delivery services | Location-based personalized offers |
| Matching Algorithms | Personalized recommendations, improved efficiency | Product suggestions, skill matching | Predictive demand forecasting |
| Blockchain | Enhanced security, transparency | Secure data management, supply chain tracking | Decentralized marketplaces |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Optimized marketplace dynamics, personalized experiences | Fraud detection, dynamic pricing | Autonomous service delivery |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Expanded asset sharing, improved utilization | Smart home rentals, connected car sharing | Real-time asset monitoring and management |
As this table shows, emerging technologies are playing an increasingly important role in facilitating various aspects of collaborative consumption. These advancements are improving efficiency, enhancing security, and opening up exciting new possibilities for sharing assets and services.
Building vs. Buying: Key Infrastructure Decisions
Launching a collaborative platform necessitates critical infrastructure decisions. Businesses face a crucial choice: build their own technology in-house or integrate pre-existing solutions. Building provides greater control but demands substantial resources and time. Buying offers a quicker path to market but may limit customization options.
The optimal approach depends on several factors, including the platform's particular needs, budgetary limits, and long-term objectives. Thoughtful consideration of these factors is vital for maximizing a platform’s chance of success. This careful planning and strategic decision-making are fundamental to building a sustainable, scalable business model. The best path forward is unique to each business and its resources.
Navigating Regulation: When Innovation Meets Legislation
The collaborative consumption business model, while offering significant economic and societal benefits, presents unique challenges for regulators. This new approach often blurs the lines between traditional business categories, requiring lawmakers to adapt existing frameworks or create entirely new ones. This section explores the complex regulatory landscape that collaborative consumption platforms must navigate.
Taxation: Grappling With New Business Models
One of the primary regulatory hurdles is taxation. Traditional tax systems struggle to categorize income generated through these platforms. Is a person renting out their spare room through Airbnb running a hotel business? Is someone driving for Uber an employee or an independent contractor? These questions highlight the ambiguity that arises when applying existing tax laws to these new business models.
This uncertainty can lead to compliance challenges for both platforms and individual participants. It's essential for platforms to provide clear guidance to their users regarding tax obligations and to work with regulators to develop appropriate tax frameworks.
Labor Classification: An Existential Threat
Labor classification is another critical area of contention. The distinction between employee and independent contractor is central to labor laws and has significant implications for worker protections and platform liability. For ride-sharing platforms, classifying drivers as employees would significantly impact their cost structure and business model.
This issue has been the subject of intense debate and litigation. Clear regulatory guidelines are needed to provide certainty for both platforms and workers. The ongoing discussions and legal battles underscore the importance of finding a balance between worker rights and the flexibility offered by the collaborative consumption model.
Insurance: Navigating a Patchwork of Requirements
Insurance requirements also vary considerably across jurisdictions. This creates a complex patchwork of regulations for platforms operating in multiple locations. Ensuring adequate insurance coverage for both providers and consumers is crucial for mitigating risk and fostering trust.
Navigating these diverse and often conflicting requirements can be a significant undertaking. The lack of standardization creates uncertainty and compliance challenges for collaborative consumption platforms. A more unified approach to insurance regulations would simplify operations and benefit the entire collaborative consumption ecosystem.
Engaging With Regulators: A Proactive Approach
Successfully navigating this regulatory landscape requires a proactive approach. Platforms must engage with regulators to address concerns and contribute to the development of appropriate legal frameworks.
This engagement can take many forms:
- Participating in public consultations
- Providing data to inform policy decisions
- Advocating for regulations that support innovation while protecting consumer interests
By actively participating in the regulatory process, platforms can help shape the future of the collaborative consumption industry.
Self-Regulation and Competitive Advantage
Some collaborative consumption platforms are exploring self-regulatory approaches. By establishing clear guidelines and standards for their operations, they aim to demonstrate responsible business practices and build trust with consumers and regulators.
This proactive approach to compliance can also differentiate a platform from competitors and even create a competitive advantage. For example, platforms that implement robust safety measures or dispute resolution mechanisms can attract users seeking reassurance and security. Transforming regulatory challenges into competitive advantages requires careful planning, transparent communication, and a genuine commitment to responsible business practices. This thoughtful engagement with regulatory complexities can ensure legal compliance and enhance platform credibility, attracting a wider user base.
Building Your Collaborative Platform: A Strategic Framework
Now it's time to bring the power of the collaborative consumption business model to your own venture. This section offers a strategic framework for building and scaling a successful platform, based on insights from founders and investors.
Initial Market Assessment: Finding Your Niche
Before you start building, understand your target market. Look for unmet needs within a specific sector that are ready for a collaborative solution. For example, maybe local musicians have difficulty finding rehearsal spaces they can afford. Identifying a niche allows you to focus your platform development and marketing efforts for early traction.
Platform Architecture: Key Decisions
Defining your platform's core functionality is essential. Will it be a peer-to-peer marketplace like Airbnb, or a subscription service offering shared resources? One helpful resource is the Ecommerce Subscription Model: Expert Strategies for Predictable Growth. Think about the technical side. Will you build your own system or use existing solutions? These architectural decisions will determine your platform's scalability and long-term viability.
Solving the Chicken-and-Egg Problem: Building Early Momentum
Many marketplaces encounter the chicken-and-egg problem: attracting both providers and users at the same time. Offering incentives to early adopters on both sides can help. For example, you could offer discounts to initial users or guarantee a certain income level for early providers to help build that critical mass. This initial momentum is key to establishing a thriving marketplace.
Monetization Models: Exploring the Options
Choosing the right monetization model is essential for financial sustainability. You have several options:
- Transaction Fees: Charge a percentage of each transaction.
- Subscriptions: Offer various access levels for recurring fees.
- Freemium: Provide basic features for free and charge for premium access.
- Advertising: Display targeted ads on the platform.
Each model has advantages and disadvantages. Transaction fees are easy to implement but might discourage high-volume transactions. Subscriptions offer predictable revenue but require compelling premium features. The best model depends on your target market and platform's functionality.
Funding and Metrics: Tracking Progress
Securing funding is often essential for scaling a collaborative consumption business. Investors look for metrics that demonstrate early traction, like user growth, transaction volume, and customer retention rates. These key performance indicators (KPIs) provide solid evidence of market demand and platform effectiveness. Tracking these KPIs is crucial for making informed decisions and attracting investment.
Learning From Successes and Failures: Avoiding Pitfalls
Studying both successful and unsuccessful collaborative consumption ventures offers valuable lessons. Understanding why some platforms struggled with trust or failed to scale can inform your own strategy. Identifying and addressing these potential issues early on can significantly improve your platform's chances of success. Building a collaborative consumption business that creates lasting value requires planning, execution, and adapting to market changes.
Ready to experience the benefits of collaborative consumption? Explore AccountShare today and discover how you can access premium services and subscriptions at a fraction of the cost. Visit AccountShare now!
