
Top IT Cost Reduction Strategies to Boost Savings in 2025
Share
Trimming IT Costs in 2025: Smart Strategies for a Leaner Budget
Optimizing IT spending is crucial for any organization or individual looking to maximize resources. This listicle delivers eight powerful IT cost reduction strategies, providing actionable insights to achieve a leaner, more efficient IT budget. We'll explore practical methods to maximize your IT investments without sacrificing performance or security.
This article goes beyond generic advice, offering fresh perspectives and specific tactics you can implement immediately. Learn how to leverage group purchasing solutions like AccountShare, optimize cloud infrastructure, and streamline processes for significant cost savings. Whether you're a tech-savvy individual, a small business owner, or a student, these strategies provide valuable tools to control IT expenses.
What You'll Learn:
- Practical IT cost reduction strategies: Discover actionable methods to optimize your IT budget.
- Group purchasing power: Explore platforms like AccountShare to lower the cost of shared services.
- Security best practices: Implement robust security measures without breaking the bank.
- Process optimization: Identify and eliminate inefficiencies in your IT workflows.
- Tool alternatives: Find cost-effective replacements for expensive software and services.
These IT cost reduction strategies address the increasing need for efficient resource allocation in today's competitive environment. Implementing these tactics can free up budget for strategic initiatives and innovation. We'll delve into specific examples and scenarios, demonstrating how each strategy can be applied for maximum impact. This detailed guide provides the knowledge and tools you need to take control of your IT spending and achieve a leaner, more effective budget.
1. Process Optimization and Automation
Process optimization and automation are cornerstones of IT cost reduction strategies. This approach involves analyzing existing IT processes, identifying inefficiencies, and streamlining operations for optimal performance. Automation complements this by introducing technology solutions to replace manual, repetitive tasks. This powerful combination reduces labor costs, minimizes human error, and accelerates processes while ensuring greater consistency. These improvements directly translate to substantial cost savings and improved productivity. This makes process optimization and automation a critical consideration for any organization seeking to control and reduce IT spending.
Examples of Successful Implementation
Several industry giants demonstrate the significant impact of process optimization and automation. Amazon’s warehouse automation has reduced fulfillment costs by a remarkable 30%, demonstrating the power of technology in optimizing complex logistics. JP Morgan's COIN system automates legal document analysis, a task previously requiring countless lawyer hours, resulting in substantial cost and time savings. Even in the fast-food industry, McDonald's has leveraged kitchen automation to improve order accuracy by a staggering 85%, minimizing waste and enhancing customer satisfaction. UPS’s ORION route optimization system has saved the company 100 million miles annually, significantly reducing fuel costs and environmental impact.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Implementing process optimization and automation effectively requires a strategic approach:
- Start Small, Focus on Impact: Begin with high-volume, repetitive processes that offer the greatest potential for cost savings and efficiency gains.
- Collaboration is Key: Involve employees in the optimization design process. Their insights into daily operations are invaluable.
- Gradual Implementation: Implement changes gradually to minimize disruption and allow for adjustments along the way.
- Measure and Refine: Measure ROI at each phase of implementation to track progress and identify areas for further improvement.
- Comprehensive Training: Provide thorough training for employees on new systems and processes to ensure successful adoption.
When and Why to Use This Approach
Process optimization and automation are particularly beneficial when dealing with:
- Repetitive Tasks: Automating repetitive tasks frees up human resources for more strategic activities.
- High-Volume Processes: Optimizing high-volume processes yields significant cost savings due to the scale of operations.
- Error-Prone Activities: Automation minimizes human error, leading to greater accuracy and reduced rework.
- Scalability Challenges: Automation allows for easier scaling of operations to meet growing demands without proportional increases in cost.
The following infographic summarizes key benefits achievable through process optimization and automation:
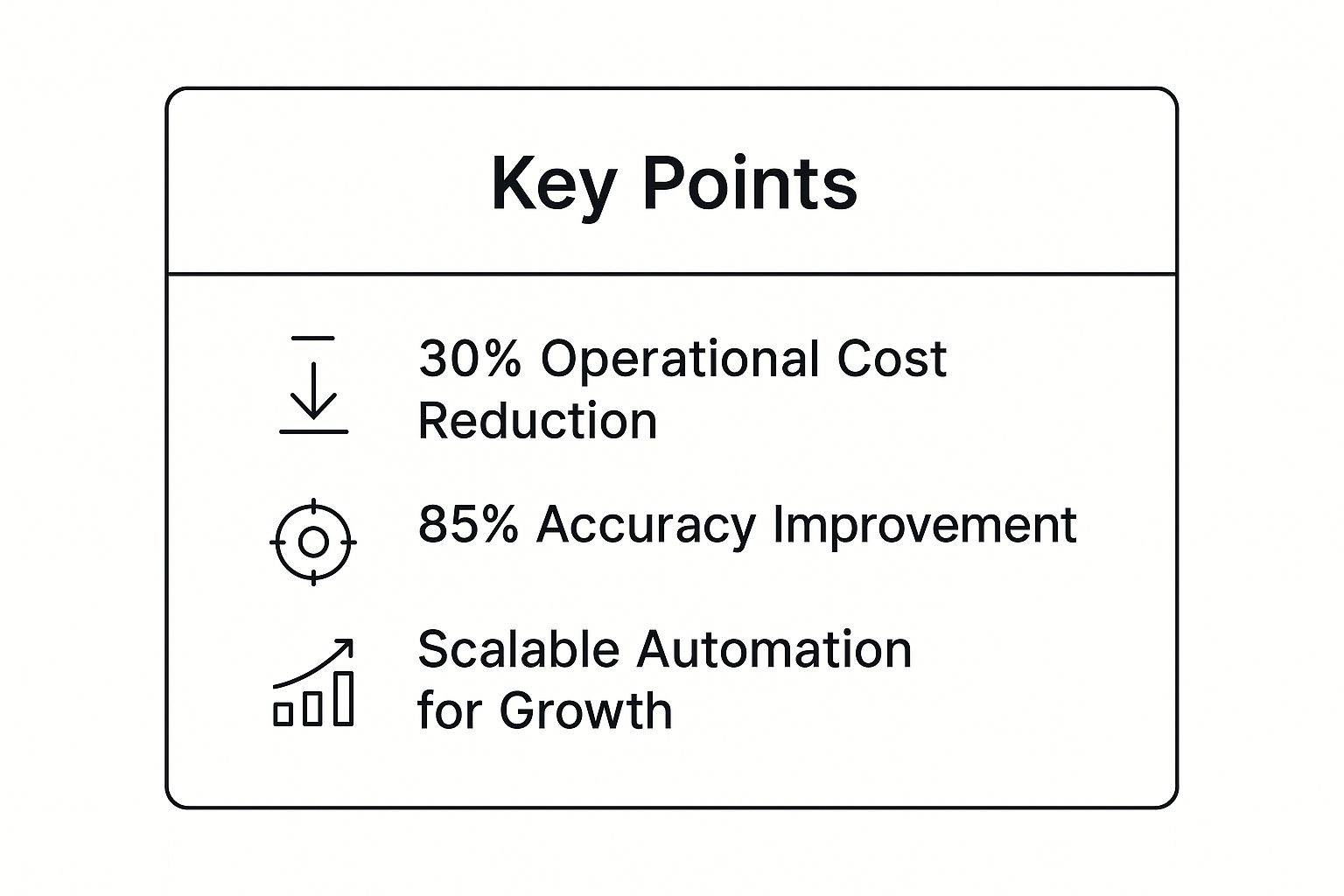
This quick-reference visualization highlights potential cost reductions of up to 30%, accuracy improvements as high as 85%, and the inherent scalability of automation to support future growth. These compelling data points underscore the transformative potential of process optimization and automation as a crucial IT cost reduction strategy. By carefully analyzing processes, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing appropriate automation solutions, organizations can significantly reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and position themselves for long-term success in a competitive landscape.
2. Strategic Sourcing and Supplier Consolidation
Strategic sourcing and supplier consolidation are powerful IT cost reduction strategies. Strategic sourcing moves beyond simple price comparisons to evaluate suppliers based on total value. This includes factors like quality, reliability, and long-term partnership potential. Supplier consolidation streamlines vendor management by reducing the number of suppliers. This allows for better pricing, simplified administration, and the development of stronger, more strategic relationships. These strategies work in tandem to optimize procurement and significantly reduce IT spending.
Examples of Successful Implementation
Industry leaders have demonstrated the substantial benefits of these approaches. Walmart, renowned for its supply chain efficiency, has saved an estimated $4 billion annually through supplier consolidation. General Electric, under Jack Welch, implemented strategic sourcing initiatives that reduced costs by 15%. Procter & Gamble streamlined its supplier base from 75,000 to 35,000, achieving significant cost savings and improved management efficiency. Boeing's strategic supplier partnerships have resulted in a 20% reduction in manufacturing costs.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Implementing strategic sourcing and supplier consolidation effectively requires careful planning and execution:
- Conduct Thorough Supplier Audits and Assessments: Evaluate current suppliers based on performance, reliability, and total cost of ownership.
- Negotiate Multi-Year Contracts: Leverage consolidated purchasing power to negotiate favorable long-term contracts with key suppliers.
- Implement Supplier Scorecards: Track supplier performance against key metrics to ensure quality and identify areas for improvement.
- Develop Backup Suppliers: Mitigate supply chain disruptions by establishing relationships with alternative suppliers.
- Focus on Total Value, Not Just Lowest Price: Consider factors like quality, reliability, and innovation potential when selecting suppliers.
When and Why to Use This Approach
Strategic sourcing and supplier consolidation are particularly effective when:
- Dealing with Multiple Suppliers: Consolidating suppliers simplifies management and improves negotiation leverage.
- Facing Increasing IT Costs: Strategic sourcing identifies opportunities for cost optimization across the supply chain.
- Seeking Long-Term Partnerships: Building strategic relationships with key suppliers fosters collaboration and innovation.
- Improving Supply Chain Efficiency: Streamlined procurement processes reduce administrative overhead and improve delivery times.
Learn more about Strategic Sourcing and Supplier Consolidation to understand the full power of this approach in your organization. By strategically selecting and managing suppliers, businesses can achieve significant IT cost reductions while enhancing quality, reliability, and overall value.
3. Cloud Migration and Infrastructure Optimization
Cloud migration and infrastructure optimization are powerful IT cost reduction strategies. This approach involves moving IT infrastructure, applications, and data from on-premises systems to cloud platforms. This transition reduces hardware costs, minimizes maintenance expenses, and provides scalable computing resources adjustable based on actual usage. These advantages lead to significant cost savings and increased operational flexibility. This makes cloud migration a crucial consideration for organizations seeking to control and reduce IT spending.

Examples of Successful Implementation
Several companies demonstrate the substantial impact of cloud migration. Netflix saved 25% on infrastructure costs by migrating to AWS, showcasing the cloud's cost-effectiveness. Capital One reduced data center costs by 40% through cloud adoption, highlighting the potential for significant savings. Spotify scaled globally while reducing IT costs by 30%, demonstrating the cloud's scalability benefits. General Electric saved $500 million through cloud transformation, underscoring the transformative potential of cloud migration.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Implementing cloud migration effectively requires a strategic approach:
- Assess Current Infrastructure: Analyze current infrastructure usage before migration to determine optimal cloud resources.
- Pilot Testing: Start with non-critical applications for pilot testing to minimize disruption and gain experience.
- Cost Monitoring: Implement proper cloud cost monitoring tools to track spending and identify optimization opportunities.
- Staff Training: Train IT staff on cloud management best practices to ensure efficient resource utilization.
- Negotiate Pricing: Negotiate enterprise-level pricing with cloud providers to secure the best possible rates.
When and Why to Use This Approach
Cloud migration is particularly beneficial when dealing with:
- High Hardware Costs: Cloud migration eliminates the need for expensive on-premises hardware.
- Scalability Needs: Cloud platforms offer flexible scalability to meet fluctuating demands.
- Maintenance Burdens: Cloud providers handle infrastructure maintenance, freeing up internal IT resources.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud platforms provide robust disaster recovery capabilities for business continuity.
- Software Updates: Cloud services often include automatic software updates, reducing management overhead.
This approach allows organizations to significantly reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. By carefully assessing needs, planning migration effectively, and implementing appropriate cloud solutions, organizations can unlock significant cost savings and operational advantages. Cloud migration is a strategic move that positions businesses for long-term success in today's dynamic technological landscape.
4. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Initiatives
Energy efficiency strategies focus on reducing energy consumption through improved equipment, processes, and behaviors while maintaining the same level of output. This translates directly into lower electricity bills and operational costs. Sustainability initiatives encompass broader environmental considerations, such as reducing waste and utilizing renewable energy sources. These efforts often result in substantial cost savings through reduced resource consumption and waste management, making them a vital component of IT cost reduction strategies.
Examples of Successful Implementation
Major corporations have demonstrated the significant financial benefits of energy efficiency and sustainability initiatives. Walmart, for instance, has saved over $1 billion annually through its aggressive energy efficiency program. Google has achieved carbon neutrality across its global operations while simultaneously reducing costs by an impressive 30%. 3M’s long-standing commitment to energy efficiency has yielded cumulative savings of $8.5 billion since 1975. IKEA has also seen substantial returns, with renewable energy investments reducing their operational costs by 25%. These real-world examples showcase the potential of energy efficiency and sustainability as potent IT cost reduction strategies.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Implementing energy efficiency and sustainability initiatives requires a well-structured approach:
- Conduct Comprehensive Energy Audits First: Identify areas of high energy consumption and potential savings opportunities within your IT infrastructure.
- Take Advantage of Utility Rebates and Tax Incentives: Many utility companies and governments offer financial incentives for implementing energy-efficient technologies.
- Implement Employee Awareness and Training Programs: Educate employees about energy-saving practices and the importance of sustainability within the organization.
- Set Measurable Sustainability Goals and Track Progress: Establish clear targets and monitor progress regularly to ensure accountability and identify areas for improvement.
- Consider Partnering with Energy Service Companies: These companies can provide expertise and assistance in implementing energy efficiency projects.
When and Why to Use This Approach
Energy efficiency and sustainability initiatives are particularly beneficial when:
- Operating Costs are High: Reducing energy consumption directly translates to lower operational expenses.
- Environmental Impact is a Concern: Sustainability initiatives align with corporate social responsibility goals and minimize environmental footprint.
- Long-Term Cost Savings are Desired: Investments in energy-efficient technologies often yield significant long-term cost savings.
- Regulatory Compliance is Necessary: Meeting environmental regulations can be achieved while simultaneously reducing costs.
Energy efficiency and sustainability initiatives offer a win-win scenario for organizations. They not only contribute to a healthier planet but also deliver tangible cost savings. By prioritizing these strategies, businesses can reduce their environmental impact, improve their bottom line, and enhance their corporate image.
5. Workforce Optimization and Remote Work
Workforce optimization and remote work represent powerful IT cost reduction strategies. This approach involves strategically managing human resources to maximize productivity and minimize expenses. Tactics include rightsizing teams, implementing remote work policies, cross-training employees, and leveraging flexible staffing models. By aligning workforce capacity with actual business demands, organizations can significantly reduce overhead costs associated with office space, utilities, and other traditional expenses. This optimized approach promotes greater agility and responsiveness to changing market conditions while simultaneously boosting employee satisfaction and work-life balance.
Examples of Successful Implementation
Several prominent companies have showcased the financial benefits of workforce optimization and remote work. Twitter, for example, saves an estimated $80 million annually through its permanent remote work policy. Shopify has reduced real estate costs by a remarkable 60% by embracing a distributed workforce. GitLab, with over 1,300 employees globally, operates entirely remotely, demonstrating the viability of this model at scale. Automattic, the company behind WordPress, also saves millions through its remote-first model. These real-world examples highlight the substantial cost savings achievable through workforce optimization and remote work strategies.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Implementing workforce optimization and remote work effectively requires a structured approach:
- Establish Clear Remote Work Policies and Expectations: Define clear guidelines for communication, availability, and performance expectations for remote employees.
- Invest in Collaboration and Communication Tools: Provide robust tools for seamless communication, project management, and virtual meetings.
- Provide Ergonomic and Technology Stipends: Offer financial support for remote workers to set up ergonomic home offices and acquire necessary technology.
- Implement Regular Virtual Team Building Activities: Foster team cohesion and morale through virtual social events and team-building exercises.
- Track Productivity Metrics Rather Than Hours Worked: Focus on outcomes and deliverables rather than traditional time-tracking methods.
When and Why to Use This Approach
Workforce optimization and remote work strategies are particularly beneficial when:
- Reducing Overhead Costs: Minimize expenses associated with physical office space, utilities, and other infrastructure costs.
- Improving Employee Flexibility and Work-Life Balance: Remote work options enhance employee satisfaction and attract top talent.
- Accessing a Wider Talent Pool: Remote work enables organizations to recruit talent beyond geographical limitations.
- Increasing Business Agility: A flexible workforce enables organizations to adapt quickly to changing market demands.
Workforce optimization combined with remote work strategies can significantly reduce IT costs and enhance overall operational efficiency. Learn more about Workforce Optimization and Remote Work at secure remote access guide to enable safe and productive remote work environments. By implementing these strategies effectively, organizations can unlock substantial cost savings, improve employee morale, and gain a competitive edge in today's dynamic business landscape.
6. Inventory Management and Just-in-Time (JIT)
Inventory management and Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory systems play a crucial role in IT cost reduction strategies. JIT aims to minimize inventory holding costs by acquiring goods only when needed in the production or service delivery process. This approach reduces waste associated with storage, obsolescence, and capital tied up in excess inventory. Improved cash flow and operational efficiency are direct results, making JIT a valuable strategy for organizations seeking to optimize their IT spending.

Examples of Successful Implementation
Several companies have demonstrated the effectiveness of JIT in reducing IT costs. Toyota's pioneering JIT system reportedly reduced inventory costs by a remarkable 75%, setting a benchmark for lean manufacturing. Dell's build-to-order model minimizes inventory holding, allowing them to respond quickly to customer demands while minimizing storage costs. Zara's fast fashion model, with its incredibly short two-week inventory cycles, exemplifies JIT in the retail sector, allowing for quick adaptation to trends and reduced overstock. Even McDonald's has optimized its supply chain using JIT principles, reducing waste by a significant 30%.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Implementing JIT effectively requires careful planning and execution:
- Start Small, Predictable Demand: Begin with high-volume, predictable demand items to gain experience and minimize risk.
- Strong Supplier Relationships: Develop close relationships with reliable suppliers to ensure timely delivery and consistent quality.
- Robust Demand Forecasting: Implement robust demand forecasting systems to accurately predict needs and avoid stockouts.
- Contingency Planning: Create contingency plans for supply disruptions to mitigate potential production or service delays.
- Monitor Inventory Turnover: Regularly monitor inventory turnover ratios to track performance and identify areas for improvement.
When and Why to Use This Approach
JIT is particularly beneficial when dealing with:
- High Storage Costs: JIT minimizes warehouse space and associated expenses, particularly relevant for bulky or specialized IT equipment.
- Rapid Technological Advancements: JIT reduces the risk of obsolescence by minimizing inventory of rapidly evolving technology components.
- Predictable Demand: JIT is most effective when demand is relatively stable and predictable, allowing for accurate forecasting.
- Strong Supplier Network: A reliable supplier network is essential for JIT to function smoothly and ensure timely delivery.
JIT inventory management, when implemented effectively, can significantly reduce IT costs by minimizing inventory holding expenses and optimizing the supply chain. By carefully analyzing demand, establishing strong supplier relationships, and implementing robust tracking systems, organizations can leverage JIT to free up valuable capital, reduce waste, and improve overall operational efficiency. This makes JIT a valuable IT cost reduction strategy, particularly in today's dynamic technological landscape.
7. Technology Consolidation and Software Optimization
Technology consolidation and software optimization are powerful IT cost reduction strategies. This approach involves reducing the number of software applications, platforms, and IT systems an organization uses. By streamlining the IT landscape, businesses can optimize the remaining solutions for maximum efficiency. This strategy eliminates redundant tools, which directly reduces licensing costs and simplifies IT management overhead while maintaining or even improving overall functionality. This makes technology consolidation a key consideration for organizations looking to trim IT spending.
Examples of Successful Implementation
Several large organizations have successfully implemented technology consolidation initiatives, demonstrating substantial cost savings. Microsoft, for instance, saved $200 million through internal software consolidation. Bank of America significantly reduced its application portfolio from 6,200 to 2,500. General Motors streamlined operations by consolidating 23 separate email systems into a single, unified platform. Coca-Cola also reaped benefits by standardizing on a single ERP system globally. These examples highlight the potential for significant savings through strategic technology consolidation.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Implementing technology consolidation and software optimization effectively requires a structured approach:
- Conduct Thorough Software Usage Analytics: Analyze software usage patterns to identify redundancies and underutilized applications. This data-driven approach ensures informed decision-making.
- Prioritize Consolidation Based on Cost-Benefit Analysis: Focus on consolidating applications that offer the greatest potential for cost savings and minimal disruption to business operations.
- Plan for Adequate Change Management and Training: Effective change management and comprehensive training are crucial for successful user adoption of new systems and processes.
- Negotiate Volume Discounts with Remaining Vendors: Leveraging consolidated software needs allows for negotiating better licensing terms and volume discounts with vendors.
- Implement Phased Rollouts to Minimize Disruption: A phased rollout approach allows for testing and adjustments, minimizing disruptions to ongoing operations during the transition.
When and Why to Use This Approach
Technology consolidation and software optimization are particularly beneficial in the following scenarios:
- Redundant Applications: Eliminate unnecessary software licenses and support costs by consolidating overlapping functionalities.
- Complex IT Infrastructure: Simplifying a complex IT infrastructure reduces management overhead and improves efficiency.
- High Software Licensing Costs: Consolidation allows for negotiating better licensing terms and reducing overall software expenditure. Learn more about enterprise license optimization to cut costs and boost compliance.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Consolidating IT systems following a merger or acquisition streamlines operations and reduces costs.
Technology consolidation and software optimization offer substantial benefits in reducing IT costs and improving operational efficiency. By strategically analyzing software usage, prioritizing consolidation efforts, and implementing changes effectively, organizations can significantly reduce their IT footprint, optimize software spending, and achieve substantial cost savings. These efforts not only contribute to a leaner IT budget but also enhance overall business agility and competitiveness.
8. Value Engineering and Design-to-Cost
Value engineering and design-to-cost are powerful IT cost reduction strategies that focus on maximizing value while minimizing expenses. Value engineering systematically analyzes IT products, services, and processes to achieve essential functions at the lowest total cost. It emphasizes maintaining quality and performance while eliminating unnecessary features or complexities. Design-to-cost, a complementary approach, sets cost targets early in the design or procurement phase. This proactive approach ensures that solutions are engineered or selected to meet these predetermined budgetary constraints. This combined approach provides a robust framework for optimizing IT spending and achieving significant cost savings.
Examples of Successful Implementation
Several organizations have successfully implemented value engineering and design-to-cost in their IT initiatives. Boeing, for example, utilized value engineering during the development of the 787 Dreamliner, reducing manufacturing costs by an estimated 20%. Ford leveraged design-to-cost principles when designing the aluminum-bodied F-150, reducing weight and cost simultaneously. Apple consistently optimizes iPhone designs, reducing component costs year after year while maintaining performance and features. General Electric, a pioneer in value engineering, has saved millions through the rigorous application of these cost-reduction principles in their jet engine development programs. These examples showcase the broad applicability and effectiveness of these strategies in managing IT budgets.
Actionable Tips for Implementation
Effective implementation of value engineering and design-to-cost requires a structured approach:
- Involve Suppliers Early: Early supplier involvement in the value engineering process can provide valuable insights and cost-saving opportunities.
- Set Clear Cost Targets: Define specific cost targets before initiating design work. This ensures that cost considerations remain a priority throughout the project lifecycle.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Employ cross-functional teams for comprehensive analysis. Diverse perspectives contribute to identifying innovative cost-saving solutions.
- Lifecycle Costs: Consider total lifecycle costs, including maintenance and support, not just initial purchase price.
- Document and Share: Document successful value engineering practices and share them across the organization to foster a culture of cost consciousness.
When and Why to Use This Approach
Value engineering and design-to-cost are particularly beneficial in the following scenarios:
- New IT Projects: Implementing these strategies during the initial stages of new projects maximizes cost-saving opportunities.
- Major System Upgrades: Value engineering can identify cost-effective alternatives during major system upgrades.
- Software Development: Design-to-cost can be integrated into software development processes to control development costs.
- Hardware Procurement: Value engineering helps identify the most cost-effective hardware solutions without compromising performance.
- Ongoing IT Operations: Regularly reviewing existing IT processes with a value engineering lens can uncover hidden cost-saving opportunities.
These proactive strategies address cost reduction strategically, ensuring that IT investments deliver maximum value while minimizing unnecessary expenditure. They empower organizations to control IT spending, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall efficiency. By incorporating value engineering and design-to-cost principles into IT planning and execution, organizations can achieve substantial long-term cost savings and improve their bottom line.
Cost Reduction Strategies Comparison
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process Optimization and Automation | High: tech integration & updates | High: automation tools & training | Reduced costs, improved accuracy & speed | High-volume, repetitive processes | Scalable, improves productivity & accuracy |
| Strategic Sourcing and Supplier Consolidation | Medium: supplier analysis & contracts | Medium: supplier audits & negotiation | Lower procurement costs, streamlined management | Procurement with multiple suppliers | Volume discounts, stronger supplier relations |
| Cloud Migration and Infrastructure Optimization | Medium to High: migration risks & planning | Medium: cloud tools & training | Cost savings, scalability, disaster recovery | IT infrastructure modernization | Lower hardware costs, flexible scaling |
| Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Initiatives | Medium: audits & behavioral change | Medium to High: equipment upgrades | Reduced utility costs, improved brand image | Operations targeting cost & environmental goals | Long-term savings, tax incentives |
| Workforce Optimization and Remote Work | Medium: new policies & tech setup | Medium: collaboration tools & training | Reduced facility costs, improved satisfaction | Organizations adopting flexible work models | Access to global talent, lower turnover |
| Inventory Management and Just-in-Time (JIT) | High: requires precise coordination | Medium: forecasting & supplier relations | Reduced carrying costs, improved cash flow | Manufacturing, retail with demand variability | Low inventory costs, waste reduction |
| Technology Consolidation and Software Optimization | Medium: system audits & integration | Medium: IT resources & training | Lower software costs, simplified IT support | Enterprises with overlapping IT systems | Cost reduction, improved security |
| Value Engineering and Design-to-Cost | High: cross-functional analysis | Medium to High: team collaboration | Lower product costs, maintained quality | Product design and manufacturing optimization | Competitive pricing, innovation under constraints |
Reaping the Rewards: A Future of Optimized IT Spending
Optimizing IT spending isn't just about cutting costs; it's about maximizing value. Throughout this article, we've explored eight key IT cost reduction strategies, ranging from process optimization and cloud migration to workforce optimization and value engineering. Each strategy offers unique opportunities to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and free up resources for strategic initiatives. By implementing these strategies effectively, organizations can achieve significant cost savings while simultaneously boosting their overall performance.
Key Takeaways for Immediate Action
Let's recap the most impactful takeaways:
- Automation: Automating repetitive tasks frees up valuable time and resources, allowing your team to focus on higher-value activities. This applies to everything from software deployment to helpdesk support.
- Strategic Sourcing: Negotiating favorable contracts with suppliers and consolidating your vendor base can dramatically reduce expenses.
- Cloud Optimization: Migrating to the cloud offers flexibility and scalability while minimizing infrastructure costs. Optimizing your cloud usage through right-sizing and reserved instances further enhances cost savings.
- Workforce Optimization: Embracing remote work models and leveraging contingent staffing can reduce overhead costs associated with office space and employee benefits.
- Software Optimization: Rationalizing your software portfolio, eliminating redundant applications, and leveraging open-source alternatives can lead to substantial cost savings.
The Power of Strategic IT Cost Management
Mastering these IT cost reduction strategies is crucial in today's competitive landscape. These strategies empower organizations to:
- Increase Profitability: Reduced IT costs directly impact the bottom line, improving profitability and financial stability.
- Enhance Innovation: Freed-up resources can be reinvested in research and development, fostering innovation and driving future growth.
- Improve Agility: Optimized IT infrastructure and processes enable organizations to respond more quickly to market changes and emerging opportunities.
- Gain a Competitive Edge: Organizations that effectively manage their IT costs are better positioned to compete in the marketplace and achieve long-term success.
Embracing the Future of IT Spending
In 2025 and beyond, smart IT spending is no longer optional; it's a necessity. By embracing a proactive and strategic approach to IT cost management, organizations can unlock significant value, drive innovation, and achieve their long-term objectives. This journey towards optimized IT spending requires continuous evaluation, adaptation, and a commitment to maximizing the return on every IT investment. The rewards, however, are substantial: a leaner, more agile, and ultimately more competitive organization.
As you explore ways to optimize your IT spending, consider the benefits of shared accounts. AccountShare offers a secure and cost-effective solution for sharing premium digital services, from streaming subscriptions to software licenses, helping you further reduce expenses and maximize the value of your subscriptions. Visit AccountShare to learn more and unlock further potential for cost savings.
