
Prevent Unauthorized Access: 10 Key Security Tips
Share
The Real Cost of Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access isn't simply a technical issue; it presents a substantial business risk with widespread consequences. Beyond the initial disruption, organizations face both tangible and intangible costs that can severely impact operations and diminish trust. This section explores the true price of security breaches, examining how unauthorized access affects organizations across various industries.
Financial Fallout: The Direct Expenses of a Breach
The most apparent cost is financial. Breaches necessitate incident response, forensic investigations, legal counsel, and potential regulatory penalties. A single data breach can cost a company millions of dollars in lost revenue, remediation efforts, and legal fees. Additionally, organizations frequently experience downtime and service disruptions, further impacting their bottom line. These direct costs can be devastating, particularly for smaller businesses lacking the resources to recover swiftly.
Reputational Damage: The Long-Term Impact on Trust
Beyond the financial strain, unauthorized access significantly damages an organization's reputation. Customers lose confidence in organizations that fail to protect their data, potentially leading to reduced customer loyalty and lost business. Negative media coverage exacerbates the damage, impacting brand image and shareholder value. Rebuilding trust after a breach is a lengthy and challenging process that demands sustained effort and open communication.
The Evolving Threat Landscape: Why Prevention Is More Critical Than Ever
Preventing unauthorized access is increasingly difficult due to the ever-changing threat landscape. Cybercriminals employ sophisticated techniques, from AI-powered phishing attacks to exploiting API vulnerabilities. In fact, preventing unauthorized access is a paramount challenge in cybersecurity, underscored by the alarming number of vulnerable web applications. A staggering 98% of web applications are vulnerable to attacks, potentially leading to malicious outcomes like malware infections and redirection to harmful websites. More detailed statistics can be found here: Learn more about cybersecurity statistics. This vulnerability necessitates organizations adopting proactive security measures to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Adapting and Thriving: How Forward-Thinking Organizations Are Responding
Forward-thinking organizations are implementing a multi-layered approach to security, integrating robust technical defenses with comprehensive employee training and awareness initiatives. Implementing stringent access controls, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring are vital steps in mitigating the risks associated with unauthorized access. Moreover, these organizations prioritize regular security assessments and penetration testing to proactively identify and address vulnerabilities. By investing in robust security measures and fostering a culture of security awareness, these organizations minimize their risk and safeguard their valuable assets.
Authentication Evolved: Beyond Passwords
Passwords, the traditional cornerstone of digital security, are no longer enough to prevent unauthorized access. Their vulnerabilities, such as being easily guessed or stolen, create a weak point in any organization's security. This demands a move towards stronger authentication methods that balance both security and a positive user experience. We need solutions that move beyond simple passwords and incorporate multiple factors.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding Layers of Security
A key step in improving authentication is implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). MFA requires users to provide several forms of identification, such as something they know (like a password), something they have (like a security token), and something they are (like biometric data). This layered approach significantly increases the difficulty for unauthorized access, even if one factor is compromised. For instance, even if a password is stolen, the attacker would still need the user's phone for the second authentication code.
You might be interested in: How to master enterprise password security
Biometrics and Behavioral Analysis: The Rise of Adaptive Authentication
Modern authentication systems are increasingly using biometrics and behavioral analysis. Biometrics, like fingerprint scanning and facial recognition using tools like Amazon Rekognition, offer convenient and secure user verification. Behavioral analysis tracks user patterns, such as typing speed and mouse movements, to detect unusual activity that might signal unauthorized access. This allows authentication to become adaptive, changing based on the context of each login.
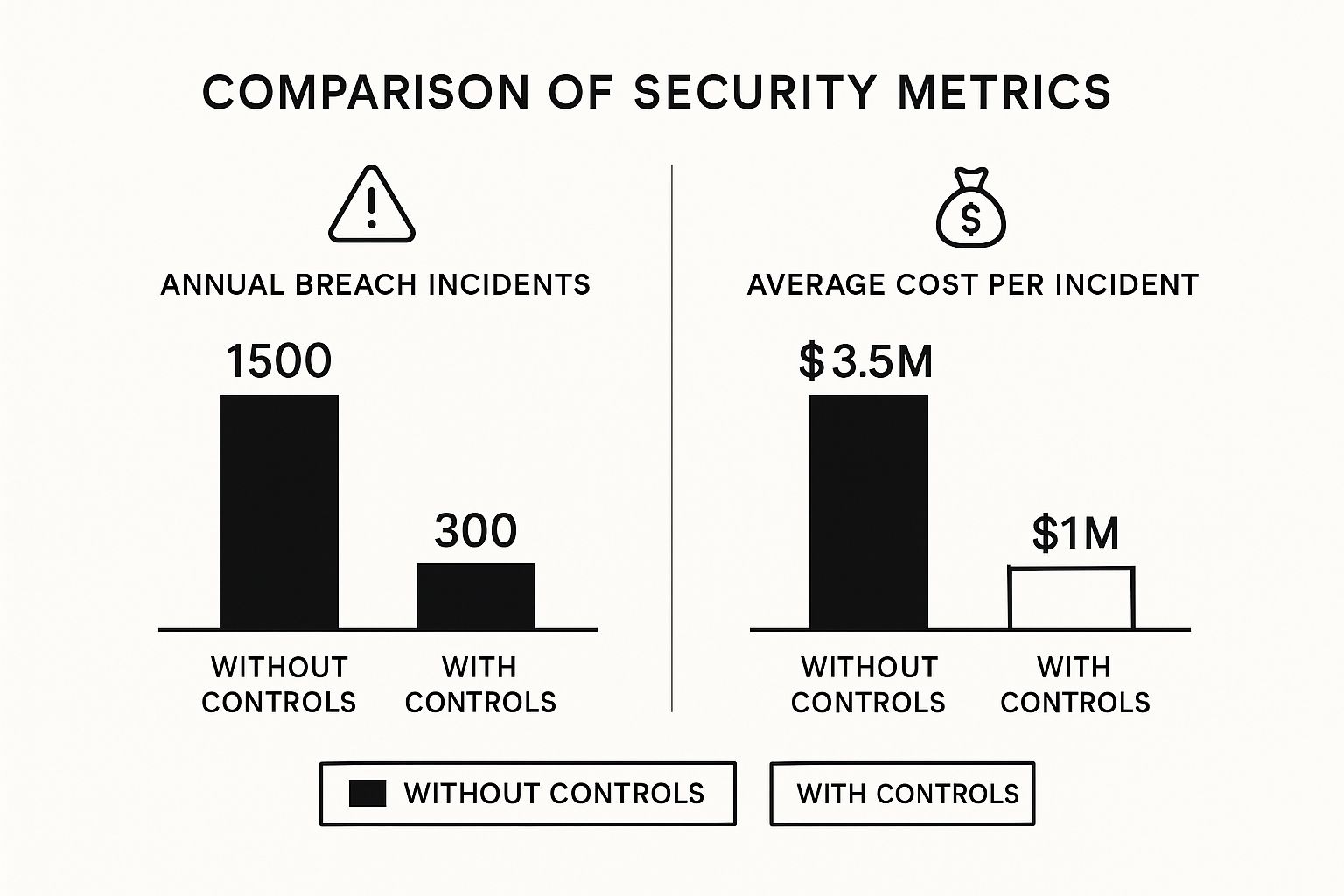
The infographic above shows the effect of strong security on data breaches and their associated costs. Robust security measures can significantly reduce the number of annual breaches from 1500 to 300 and lower the average cost per incident from $3.5 million to $1 million. These numbers highlight the importance of investing in security to prevent unauthorized access. However, this strong defense must be balanced with user-friendliness.
Contextual Factors: Adding Another Dimension to Security
Another critical aspect of modern authentication is considering contextual factors. This includes looking at the user's location, device, and login time. For example, a login attempt from an unusual location or a new device could trigger extra verification steps. This adds another security layer, making it more challenging for attackers to impersonate legitimate users. DDoS attacks and botnets also pose a significant risk, using automated access attempts to overwhelm defenses. The 41% increase in DDoS attacks in 2024 demonstrates the increasing complexity of these threats. You can find more detailed statistics here: Learn more about cybersecurity statistics. Preventing unauthorized access requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses both human and automated threats.
To further illustrate the differences between authentication methods, let's examine the following comparison:
Authentication Methods Comparison This table compares different authentication methods based on security level, user experience, implementation complexity, and cost.
| Authentication Method | Security Level | User Experience | Implementation Complexity | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Password Only | Low | Simple | Easy | Low |
| Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | Medium | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | High | Moderate | Complex | High |
| Biometrics | High | Convenient | Complex | High |
| Behavioral Analysis | Medium | Seamless | Complex | High |
Key takeaways from this comparison include the trade-offs between security and user experience. While password-only authentication is simple for users, it offers weak security. MFA provides the strongest security but can be more complex for users. Biometrics offers a balance of strong security and convenience, but the implementation can be complex and costly. Choosing the right authentication method depends on balancing the specific security needs of an organization with the user experience.
Mastering Access Control: The Right Privileges

Effective access control is the foundation of a secure organization. It's a delicate balancing act between safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring smooth, productive workflows. Too many restrictions can stifle productivity, while too few can leave your organization exposed to risk. This section explores how successful organizations implement the principle of least privilege effectively.
The Principle of Least Privilege: A Foundation for Security
The principle of least privilege is a fundamental security concept. It states that users and systems should only have access to the specific data and resources necessary to perform their assigned tasks. This principle significantly reduces the potential damage from compromised accounts or insider threats.
For example, a marketing team member doesn't need access to sensitive financial records. Similarly, a software developer shouldn't have administrative privileges on live servers unless absolutely essential. This compartmentalization of access limits the impact of any potential security breach.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Scaling Security Effectively
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a highly effective method for implementing the principle of least privilege. RBAC simplifies access management by assigning permissions to specific roles rather than individual users. Users are then assigned to roles based on their job functions.
This approach automates access adjustments when employees change roles, reducing administrative overhead and strengthening security. RBAC is especially valuable in larger organizations where managing individual permissions can quickly become complex.
You might be interested in: How to master effective group access control
Conducting Effective Access Reviews: Staying Ahead of Threats
Regular access reviews are vital for maintaining a robust security posture. These reviews help identify and remove unnecessary access, ensuring that permissions align with current job responsibilities. This proactive approach prevents unauthorized access that can arise from employees changing roles or leaving the organization.
Furthermore, regular reviews can uncover dormant accounts, a common target for attackers. By identifying and disabling these accounts, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability.
Governance and Privileged Access Management: Maintaining Control
Establishing strong governance processes is paramount for long-term success in preventing unauthorized access. This includes clear policies for access requests, approvals, and reviews. These policies ensure accountability and transparency in managing access rights.
A crucial aspect of governance is Privileged Access Management (PAM), which focuses on controlling access to highly sensitive systems and data. PAM solutions often include advanced security measures like session recording and auditing to monitor and track privileged activities. This adds a critical layer of defense against malicious insiders or external attackers who compromise privileged accounts. Traditional PAM solutions that solely focus on initial access points are no longer adequate. Modern PAM requires granular control over user actions within critical resources and continuous risk assessment.
Building Network Defenses That Actually Work

Your network is under constant attack. Threats loom large, demanding strong defenses to keep unauthorized users out. A simple firewall just doesn't cut it anymore. This section explores how organizations are building multi-layered network security that truly delivers. We'll go beyond the basics and explore practical strategies to strengthen your network.
Network Segmentation: Containing the Damage
Network segmentation is a crucial first step. This involves splitting your network into smaller, isolated sections. Think of it like bulkheads on a ship. If one compartment floods, the others remain sealed, preventing the ship from sinking. Similarly, if one network segment is compromised, the attacker's movement is restricted. They can't easily spread across your entire network. This containment strategy minimizes the fallout from a breach. For instance, isolating your finance department's network from your marketing team's network limits the impact of a security incident.
Zero Trust Architecture: Verify, Then Trust
Forget "trust but verify." Zero trust architecture is the new standard. This security model assumes no inherent trust. Instead, it requires verification at every single access point. This means confirming the user, their device, and the specific application before granting access to any resource. This strict verification significantly lowers the risk of unauthorized access. Even users and devices already inside the network perimeter aren't automatically trusted.
Advanced Traffic Monitoring: Identifying Suspicious Activity
Modern network defenses rely on advanced traffic monitoring. These systems go far beyond basic intrusion detection. They analyze network traffic patterns to pinpoint anomalies and potential threats. This could involve looking for unusual login attempts, strange data transfers, or suspicious access requests. These systems give security teams a real-time view of network activity, enabling swift responses to potential breaches and stopping unauthorized access before it escalates.
Prioritizing Protection: Identifying and Securing Vulnerable Points
Understanding your vulnerabilities is key to effective network security. You need to know where your network is weakest to prioritize your defenses. This often involves regular vulnerability scanning and penetration testing to uncover weaknesses. Once these weak points are identified, you can focus resources on bolstering these areas for maximum impact.
Real-World Implementations and Lessons Learned
Looking at both successful network defenses and high-profile failures offers invaluable lessons. Case studies provide real-world examples of how specific configurations and architectural approaches have performed across different industries. This practical knowledge can guide your security strategy, allowing you to adapt best practices to your organization's specific needs. For example, understanding how a company successfully implemented microsegmentation can inform your own implementation. This detailed approach creates highly granular security zones within the network, further preventing unauthorized access.
Building effective network defenses requires a multi-pronged approach. It's a blend of technology, strategy, and continuous adaptation. By implementing these techniques, you can create a strong security posture that effectively blocks unauthorized access and protects your organization from increasingly complex threats.
Encryption Strategies: Protecting What Matters Most
When other security measures fail, encryption acts as the last line of defense. This section explores encryption technologies and how organizations use them to protect data, even after perimeter breaches. We'll examine how to build an encryption strategy that safeguards sensitive information without impacting operations.
Understanding Encryption Basics: A Simple Analogy
Imagine sending a locked box through the mail. Only the recipient with the correct key can open it and access the contents. Similarly, encryption scrambles data, making it unreadable. Only authorized parties with the decryption key can restore the data to its original form. This ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access, the data remains unusable.
Key Management: The Cornerstone of Effective Encryption
Effective encryption depends on robust key management. This includes secure key generation, storage, rotation, and revocation. Think of your encryption keys as the master keys to your most valuable assets. Protecting them is paramount. Strong key management practices ensure keys are never compromised, which would render the encryption useless. Organizations must carefully consider their key management approach, whether using dedicated hardware security modules (HSMs) or cloud-based key management systems.
Encryption in Action: Data at Rest and in Transit
Encryption applies to data both at rest and in transit. Data at rest refers to data stored on devices or in databases. Encrypting this data protects it even if a device is stolen or a server is compromised. Data in transit refers to data moving across networks. Encrypting data in transit protects it from eavesdropping and tampering. For instance, HTTPS encrypts data transmitted between a user's browser and a website. To build strong network defenses, consider integrating security practices early in development, as discussed in this article on Secure Code Integration. This proactive approach builds security into your systems' foundation.
Data Classification: Prioritizing Protection Efforts
Not all data is equally important. A data classification framework helps organizations categorize data by sensitivity. This allows for prioritizing encryption efforts and applying appropriate protection levels. For example, highly sensitive data like customer payment information needs stronger encryption than less critical data.
Encryption in the Cloud: Navigating Shared Responsibility
In cloud environments, understanding the shared responsibility model is essential. Cloud providers secure the underlying infrastructure, while organizations protect their data within the cloud. This necessitates careful consideration of encryption options offered by cloud providers and implementing suitable key management strategies.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
Implementing encryption can be challenging. Common pitfalls include weak key management, improper implementation, and a lack of a clear encryption strategy. Best practices include using strong encryption algorithms, regular key rotation, and robust access controls for key management systems. These steps maximize encryption effectiveness. Also, ensure your encryption strategy aligns with industry best practices and any relevant compliance requirements.
Creating a Human Firewall: Beyond Basic Training

Your employees are your greatest asset, but also a potential vulnerability in cybersecurity. While strong technical defenses are essential, a security-conscious workforce acts as an invaluable human firewall. This section explores strategies to go beyond basic training and create a robust security culture within your organization.
From Checkboxes to Culture: Rethinking Security Awareness
Traditional security training programs often prioritize compliance over actual behavioral change. This "checkbox" mentality can leave organizations exposed. Instead, build a culture where security is everyone's shared responsibility.
Foster a sense of ownership and empower employees to actively participate in protecting company data. Encourage them to report anything suspicious, no matter how insignificant it may seem.
Engaging Training That Sticks: Leveraging Behavioral Science
Effective training utilizes principles of behavioral science to create lasting change. Interactive exercises, real-world examples, and storytelling make learning more engaging. Gamification and reward systems can further motivate employees to adopt security best practices. This transforms security training from a chore into a relevant and engaging experience.
Measuring Effectiveness: Beyond Completion Rates
Simply tracking course completion isn't enough. True effectiveness lies in measurable behavior change. Regular phishing simulations are invaluable for assessing employee responses to real-world threats. Analyze the results to pinpoint areas for improvement and refine your training accordingly. This data-driven approach helps continually strengthen your human firewall.
Realistic Security Simulations: Putting Knowledge to the Test
Regular security simulations, such as simulated phishing attacks, are key to reinforcing training and identifying weaknesses. These exercises offer practical experience in recognizing and responding to threats. They also highlight areas requiring further training, enabling you to proactively address vulnerabilities.
Maintaining Ongoing Awareness: Keeping Security Top of Mind
Security awareness isn't a one-time activity. Consistent communication, reminders, and updates are vital. Utilize a variety of channels, like newsletters, posters, and short videos, to reinforce key messages and inform employees about emerging threats. This regular reinforcement cultivates a strong and enduring security culture.
Addressing the Challenges of Remote and Hybrid Workforces
The increasing prevalence of remote and hybrid work environments presents unique security challenges. Employees accessing company resources from diverse locations and devices expand the potential attack surface. Address these challenges with clear policies for remote access, secure device management, and regular security awareness reminders specific to remote work. This helps maintain a consistent level of security across all locations. Your employees are your first line of defense, and comprehensive security awareness training is crucial.
Detecting and Responding to Access Threats
Preventing unauthorized access is like safeguarding a valuable treasure. Strong defenses, like authentication and access controls, are crucial, but constant vigilance and a swift response to potential threats are equally important. This section explores how security-conscious organizations detect and respond to access threats, turning potential breaches into manageable incidents.
Establishing a Baseline: Understanding Normal Behavior
The foundation of effective threat detection lies in understanding what constitutes "normal" activity within your systems. This involves establishing behavioral baselines for users, applications, and network traffic. This baseline serves as a benchmark against which future activity is measured. Any significant deviation, such as a sudden increase in data downloads from a specific user account, could indicate a compromised account and serve as an early warning sign of unauthorized access.
Monitoring and Alerting: Real-Time Threat Detection
Continuous monitoring is the lifeblood of a robust security system. Real-time monitoring systems, such as those offered by Splunk, analyze network traffic, user activity, and system logs for unusual patterns that suggest unauthorized access attempts. They look for indicators like failed login attempts, access to sensitive data outside of regular working hours, or atypical data transfer activity. These systems trigger alerts to inform the security team of potential threats, enabling a rapid response to prevent further damage.
Security Orchestration and Automation: Streamlining Incident Response
Responding effectively to access threats demands speed and efficiency. Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) tools automate security tasks and incident response workflows. For example, a SOAR system can automatically block a suspicious IP address, isolate a compromised system, or initiate a security scan upon detecting unusual activity. This swift, automated response significantly minimizes the impact of access threats. Read also: How to master secure password sharing. This automation allows security teams to focus on more complex investigations and strategic security enhancements.
Incident Response Playbooks: Prepared for Any Scenario
Much like firefighters have procedures for different types of emergencies, organizations need specific incident response playbooks for various access violation scenarios. These playbooks detail the step-by-step actions to take in case of a suspected or confirmed breach. A well-defined playbook ensures a consistent and efficient response, reducing downtime and damage. They establish clear roles and responsibilities, ensuring that the appropriate security measures are implemented quickly. This preparation is essential for a coordinated and effective response.
Threat Hunting and Post-Incident Analysis: Continuously Improving Security
Threat hunting involves proactively searching for hidden or emerging threats that may have circumvented existing security measures. This proactive approach goes beyond reactive incident response, aiming to identify potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Post-incident analysis examines past incidents to understand the root causes, weaknesses in defenses, and areas for improvement. Both threat hunting and post-incident analysis are critical for continually strengthening security posture and building a more resilient security framework. Comprehensive security awareness training for employees, your first line of defense, is also vital.
To better understand the importance of quick action, let's review the following table:
Unauthorized Access Indicators and Response Actions This table presents common indicators of unauthorized access attempts and the appropriate response actions for each scenario
| Indicator | Severity Level | Immediate Actions | Follow-up Steps | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple failed login attempts | Medium | Lock the account temporarily | Investigate the source of the attempts | Implement multi-factor authentication |
| Access to sensitive data outside normal hours | High | Revoke access immediately | Conduct a full security audit | Implement strong access controls |
| Unusual data transfer activity | High | Block the transfer | Investigate the destination and purpose of the transfer | Monitor network traffic for anomalies |
By integrating proactive measures like establishing baselines and reactive responses guided by playbooks, organizations can considerably reduce the risk and impact of unauthorized access. This vigilance is essential in navigating today's intricate threat landscape.
